Healthy food >>>> Freezing technology for vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, roots
Freezing technology for vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, roots.
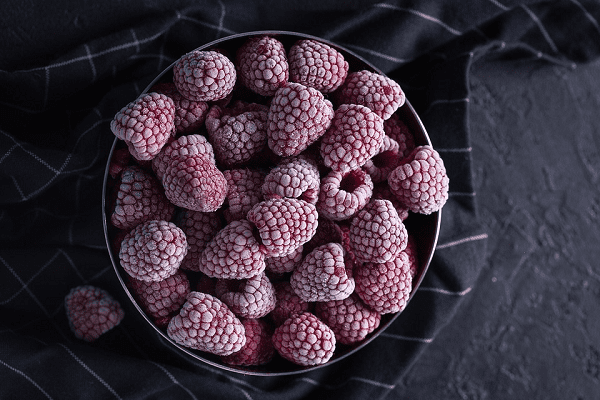
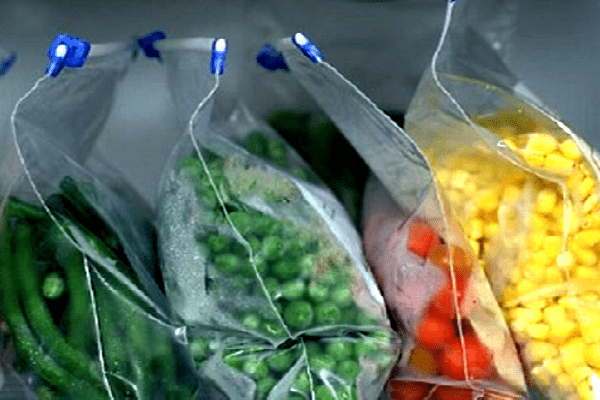


Freezing of fruits, leaves, stems and roots of plants is considered the most profitable and less laborious way of storing food for future use in comparison with drying and canning. Almost any plant and its constituent parts can be frozen and preserved for the winter diet.
There are two ways to freeze plants: dry and ice. In dry freezing, plant parts are kept in their natural state. When frozen in ice, parts of plants are frozen into ice (in ice forms).


To prevent frozen fruits, leaves, roots and stems from spreading after defrosting, it is necessary to master several principles of freezing vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, roots:
- Any component parts of the plant before dry freezing should be washed and dried well so that they do not have to be washed after thawing, which creates the prerequisites for disrupting the integrity of the tissues of the thawed plant.
- Water in an insufficiently dried plant at low temperatures will begin to crystallize, will cause sticking of plant blanks and make it difficult to separate them into portions.
- Draining berries and fruits (pieces of fruit) are laid out on paper towels to dry before freezing.
- To make the preparations of berries and pieces of fruit sweeter after defrosting, it is recommended to roll each piece, berry (previously dried) in sugar.
- Vegetables, herbs, roots, finely chopped or grated on a coarse grater, can be salted before freezing (to the taste and habits of the supplier).
- It is better to freeze edible plant roots in a cut form, since during the entire freezing time the water component will freeze from the roots, which will lead to increased root rigidity and make it almost impossible to divide it into small parts.
- Some plants recommend boiling for a few minutes before freezing (peas, beans, corn, mushrooms, carrots, beets).
- It is convenient to freeze fruit, berry or vegetable mixes (mixtures) so that you do not have to defrost several different portions of plants.
- To freeze soft vegetables, berries and fruits, you can use not bags, but disposable plastic containers with lids, which can be folded in portions (in small bags).
- Defrosting and subsequent freezing are unacceptable to preserve the integrity and usefulness of plant preparations, for this reason they are frozen in portions.
- The ideal freezing of vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, roots is freezing at a fast pace, when the temperature in the freezer has already reached its maximum.
- Plants are thawed - gradually.
- Thawed plants are boiled several times faster than fresh ones.
- When frozen in ice molds, it does not matter how dry the ingredient is.

There are several ways to freeze greens in portions: cut into small portions in a container of the appropriate size; completely wrapped (along the entire length of the plant) in a briquette, followed by cutting when defrosting; frozen portioned ice molds.
Which green vegetables are frozen (greens):
- Head fennel (heads of cabbage, half heads, quarters of heads);
- Leafy fennel (chopped greens and stems)
- Head chicory "Vitluf" (heads of cabbage, half heads, quarters of heads of cabbage);
- Onion feathers (whole or chopped);
- Amaranth leaves (whole);
- Basil leaves (whole);
- Lettuce leaves (whole or chopped);
- Parsley leaves (whole)
- Dill leaves (chopped or whole);
- Rucola leaves (whole or cut);
- Spinach leaves (whole or chopped)
- Chard leaves and stems (chopped);
- Purslane leaves (whole);
- Rosemary leaves (whole or chopped)
- Marjoram leaves (whole).
Which plant stems are frozen:
- Asparagus (whole or sliced)
- Celery stalk (chopped)
- Rhubarb (sliced);
- Dill stalks (chopped);
- Garlic stalks (chopped);
- Purslane stalks (sliced).
Which plant roots are frozen:
- Celery root (rings, slices, cubes);
- Horseradish root (in circles, stripes, shabby on a coarse grater);
- Root parsley (cut into rings, strips or tinder on a coarse grater);
- Ginger root (cut into circles, cubes, coarse grated);
- Parsnip root (sliced, diced, grated);
- Valerian root (in circles, grated);
- Ginseng root (sliced, grated).
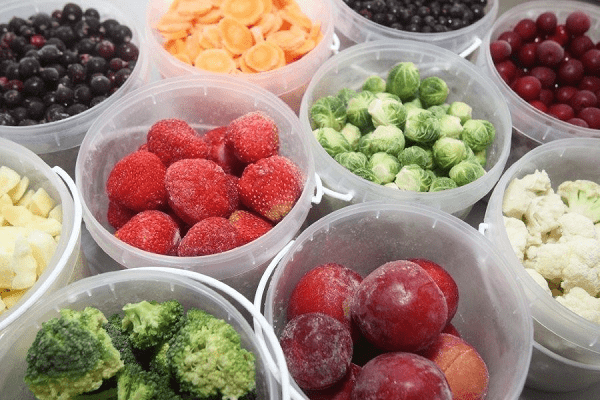

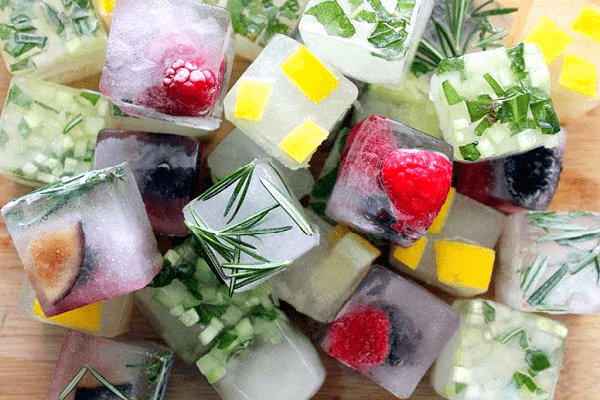
Which vegetables are frozen:
- Carrots (cut into circles, strips, cubes, grated on a coarse grater);
- Beets (cut into large pieces, strips or cubes, grated);
- Turnip (cut into circles or cubes, grated);
- Radish (cut into circles or cubes);
- Daikon (cut into circles or cubes);
- Zucchini (cut into large pieces, cubes, circles, slices);
- Eggplants (cut into large pieces, cubes, circles, slices);
- Bulgarian pepper (cut into rings or slices, whole without seeds and tail);
- Tomatoes (in circles, "Cheri" whole - you can with a puncture);
- Cucumbers (cut into circles, slices, large pieces);
- Pumpkin (cut into large or small pieces, grated on a coarse grater);
- Cauliflower and broccoli (divided into small inflorescences, the legs are cut into large pieces);
- Kohlrabi cabbage (cut into circles, slices, cubes);
- Brussels sprouts (cabbage or half cabbage);
- White cabbage or Savoy cabbage (chopped leaves, quarters of medium-sized heads of cabbage);
- Artichoke (heads of cabbage, half heads, quarters of heads of cabbage);
- Beans, peas (grains or pods);
- Corn (grains, young small ears - chopped or whole);
- Mushrooms (large - in pieces, small and medium - whole).
What fruits and berries are frozen:
- Plums (whole and slices);
- Apricots (halves or slices);
- Peaches (halves or slices);
- Kiwi (halves or slices);
- Banana (peeled and cut into circles or strips);
- Cherries and cherries (whole);
- Citrus fruits (slices);
- Melon (slices);
- Pears and quince (in slices);
- Grapes (berries);
- Raspberry, blackberry, mulberry (whole);
- Currants, blueberries, gooseberries, sea buckthorn (whole);
- Strawberries, strawberries (whole);
- Cranberries, cloudberries, drupes, thorns (whole);
- Apples (slices);
- Figs (halves or slices).
Freezing in ice molds is carried out using ice molds (large-mesh), frost-resistant plastic and silicone molds. Frozen ice cubes (ice molds) with "filling" are put in bags or plastic frost-resistant containers and stored in the same way as ordinary ice.
Freezing in ice molds has its advantages and disadvantages:
- it is impossible to freeze in large portions - only one or several berries, pieces of fruits (stems, leaves) of a vegetable ingredient;
- plants frozen in ice and intended for a raw food diet take a long time to thaw;
- large quantities of ice molds cannot be placed compactly (they will take up a lot of space in the freezer);
- look beautiful when decorating dishes or drinks;
- can be used as an independent dessert (instead of ice cream);
- convenient for making soft drinks, lemonades and cold soups (vegetable soup, beetroot soup, tomato soup).
What vitamins are lost when frozen? It makes sense to freeze only those fruits, leaves, stems and roots of plants that were plucked shortly before harvesting, since useful components are destroyed in plants that have been plucked for a long time.
The most unstable to low temperatures are B vitamins and vitamin A (beta-carotene). Vitamin C retains its qualities to a greater extent, but after defrosting it quickly degrades. Vitamin E is most resistant to low temperatures. These facts must be taken into account, and there are defrosted vegetables, fruits and berries immediately after defrosting.

Read

Read



























