Interesting >>>> Ortholens
Ortholens.

Ortholens (in other words, orthokeratological therapy) are gaining momentum today due to the great demand for methods of correcting and slowing down the development of myopia and astigmatism, which are associated with violations of the refractive properties of the cornea of the eye.
The orthokeratological method of treating myopia and the diseases that it accompanies is based on the effect of redistributed pressure on the surface, forcing it to change refraction (the bulge of the cornea is what achieves the desired result). The idea of physical impact on the cornea appeared a long time ago, back in the 80s of the 20th century, but it was possible to implement it quite recently.
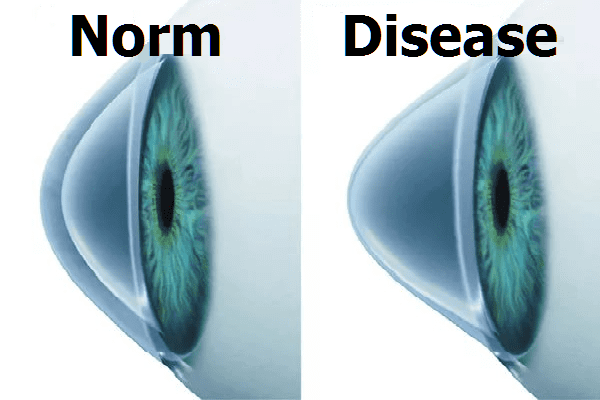
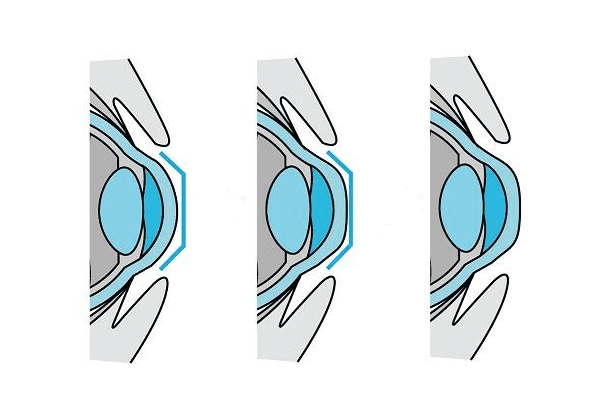
The advent of contact lenses has greatly facilitated the task of creating conditions for selective pressure on certain parts of the cornea for a long time, which makes it possible to achieve a temporary but rather long-lasting effect of changing corneal refraction as a result of forced pressure. This is how night lenses (ortholens) appeared that have special convex areas that coincide with the convexity of the cornea. The lenses apply continuous pressure to the desired areas and relieve those areas where pressure should not be distributed. While a person is sleeping (eyes are closed), the lens "deforms", flattens the refractive bend of the cornea, and this flattening is enough for the entire next day of wakefulness without glasses and lenses to compensate for myopia. Then the effect must be repeated, putting on night lenses and straightening the bulge of the cornea for the next day of work of the visual apparatus.
During the test wearing of night lenses, it was noticed that the rate of development of myopia begins to decrease by a factor of two or more, which very favorably distinguishes the technique of night lenses from wearing glasses and ordinary lenses, in which the problem of poor vision is solved temporarily and, moreover, with each aggravated by the year, since nothing forces the refractive abilities of the cornea to change, but on the contrary weakens the muscles that bend the contour of the cornea.
This physical pressure on the cornea stimulates the corneal epithelium to renew itself in those places that are experiencing the greatest pressure in the center of the cornea and around its periphery. Since the effect of the technique is reversible, there is no danger of corneal deformation. But the only condition for obtaining a healthy effect is the lacrimal layer between the lens and the cornea under pressure on it, that is, pressure should be exerted indirectly: on the cornea, but through the lacrimal layer, otherwise the development of corneal trauma is inevitable and, as a consequence, keratosis.
The technique of wearing night lenses with an orthokeratological effect is attractive for those age categories for whom surgical refractive vision correction is not indicated due to age restrictions or for other reasons.
Orthokeratology makes it possible to do without means of vision correction during the active daytime period, and during sleep it is possible to simulate corneal refraction without stress.
The problem of vision loss, and in particular the development of myopia, is associated not only with hereditary, age-related causes. A great burden on the visual apparatus today is exerted by addictions to reading and viewing texts and small pictures from mobile devices - prolonged loads of electronic gadgets provoke refractive changes in the cornea, which is aggravated every year. Not everyone agrees to the surgical correction of myopia, and during the period of age-related changes in the functioning of the visual apparatus, this is almost impossible. But orthokeratology gives people with vision problems a chance to improve their health and lead a comfortable lifestyle, not tied to wearing additional vision correction means.
The disadvantages of wearing glasses and regular lenses are obvious:
- interfere with peripheral vision,
- require additional care,
- uncomfortable on the road,
- tired eyes, regardless of the healing effect,
- distort images to some extent.
Good to know about night lenses:
In contrast to conventional vision aids, ortholens do not interfere with anything. The inconvenience of ortholens lies only in the fact that in order to achieve obvious signs of improved vision, the lenses must be worn for 8-9 hours (that is, 8-9 hours of sleep), and for people who sleep for 4-7 hours, the results will be worse: during the day, vision will be restored , but in the long term, for people with poor vision, a decrease in the rate of progression of myopia may not have the expected effect.
The effect of a decrease in the rate of development of myopia is observed only with regular wearing of night lenses for several months.
Orthokeratological lenses are individually made lenses that take into account all the nuances of refractive disorders of the cornea. For individual selection of ortholens, orthokeratotopography, keratometry are performed (sometimes ultrasound of the eyeball and the fundus of the cornea of the eye, when the smallest changes in the curvature of the corneal area are detected).
Ortholens are much tougher than conventional corrective lenses and feel like a foreign body, but only when the eyes are open. When the eyes are closed, the hardness of the lens is not felt. Ortholens are put on before going to bed and removed immediately after waking up. In each case, the lenses are tested in the doctor's office: the patient puts on the lenses and sits for at least half an hour to initiate exposure to the cornea. The effect is noticeable almost immediately, it is finally possible to get used to the lenses after two weeks of use at night. The therapeutic effect of wearing ortholens will be noticeable the very next day after sleep. Night lenses are stored, as usual, in a specially designed liquid and in a closed container.
Ortholens (night lenses) are reusable lenses, but after the period planned by the doctor, they must be renewed taking into account the new conditions of the state of vision.
In case of myopia, night lenses correct vision up to 6-8 diopters, with farsightedness they correct up to plus 4 diopters, and with astigmatism up to 1.51 diopters.
Ortholens are shown to people from seven to forty years old or until the time when age-related presbyopia begins to develop.
Contraindications to wearing ortholens:
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye,
- the peak period of acute respiratory infections, accompanied by lacrimation,
- all infectious diseases of the eye (mucous membranes of the eyelids, eyeball), chronic or acute,
- corneal injury,
- chronic diseases: dry eye syndrome, cataracts, glaucoma,
- physiological disorders of the visual apparatus (strabismus, presbyopia, keratoconus, keratoglobus),
- period of pregnancy.
The most common side effects of wearing night lenses are inflammation of the conjunctiva, redness of the sclera - these effects can be the result of insufficient secretion of tear secretions.

Read

Read



























