Antiseptics and antibiotics >>>> Disinfectants and antiseptics for the treatment of hands
Disinfectants and antiseptics for the treatment of hands.
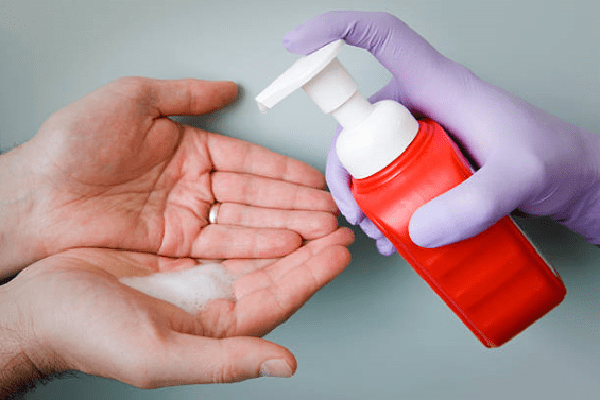
Hand washing is considered an essential method of preventing the spread of infection . There are three levels of hand disinfection: household, hygienic, and surgical.
At the household level, hand washing is a process of combating transient microflora with water and soap, and it must be carried out before eating or feeding, working with food; after visiting the washrooms, after caring for a patient, after any degree of hand contamination.
Hygienic hand washing involves the use of antiseptic agents for washing, effectively removing transient microorganisms. Hand hygienic treatment is carried out before and after invasive procedures (injections - operations); before caring for a patient with reduced immunity; before and after caring for a wound or using a urinary catheter; before and after putting on disposable gloves; after contact with body fluids or suspected microbial contamination.
Surgical level of hand treatment aims to eliminate transient microorganisms and reduce the level of resident microorganisms in the event of the risk of contamination of the surgical wound if gloves are damaged. Antiseptics containing alcohols are used.
There are two types of hand antiseptics:
- Water with the addition of surfactants (surfactants) - soaps, powders, gels, pastes;
- Alcohols (more effective than water based) are commonly used by nurses and surgeons.
Alcohol-based skin antiseptics:
- 0.5% alcoholic solution of chlorhexidine in 70% alcohol isopropanol or ethanol;
- 60% isopropanol solution or 70% ethanol solution plus skin softening additives;
- Complex of 60% isopropyl alcohols with perfume and hand softening additives - "MANOPRONTO-EXTRA";
- 0.5% chlorhexidine solution plus alcohols, emollients and perfume - "BIOTENZID";
- VELTOSEPT - clathrate of a quaternary ammonium compound with urea plus isopropyl alcohol;
- SEPTOCID R PLUS - 0, 115% butanediol, 5% isopropyl alcohol (propanol-2), 68.229% ethyl alcohol (ethanol), emollients;
- "AHD-2000 SPECIAL" - 0.5% chlorhexidine bigluconate, 78% ethyl alcohol (ethanol), excipients;
- OCTINIDERM - 30% 1-propanol, 45% 2-propanol and 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride.
Stages of correct hand treatment:
- Nails should be cleaned (or cut short by the nursing staff), rings and watches are removed before hand washing, cuts and scratches are sealed with waterproof dressings.
- Hands are washed thoroughly, even if they were wearing gloves, as a violation of the integrity of the gloves may go unnoticed. Hands are moistened with water, soap or an antiseptic agent is applied, and vigorous movements alternately rub the palms and backs of the hands.
- Next, the interdigital spaces, phalanges and fingertips are carefully processed. They try not to spray water or disinfectant, since microorganisms can scatter with droplets of the substance and settle on clothes and surrounding objects. When washing hands with water, the wrists are also captured.
- The remains of the soap solution are washed off with water (the antiseptic is not washed off).
- Drying your hands with an automatic dryer or disposable paper towels is considered the safest and most hygienic condition.

Read

Read



























