Andrology - male diseases >>>> How is phimosis treated?
How is phimosis treated?

A prepuce or foreskin is a fold of skin that completely covers the glans of the penis and slides to expose the glans during erection. The foreskin is the protection of the mucous membrane of the glans penis from excessive drying out and external influences. In certain cases, the foreskin is formed in such a way that it turns out to be much narrower (smaller in volume), fits the head tighter than necessary, which makes it difficult for the glans penis to pass. In such cases, they speak of phimosis (or, more precisely, atrophic phimosis). There is also hypertrophic phimosis, when the foreskin is longer than the anatomical structure of the penis and glans requires, it extends beyond the glans and resembles a proboscis.
Phimosis is not uncommon, and often the prepuce remains tight until puberty, and this is not considered a pathology. About the pathology of the prepuce (that is, phimosis) is said when this problem interferes with the exit of the head during the erection period and causes painful sensations. As a rule, phimosis in childhood does not require any significant corrections, but rather more careful care of the genitals and waiting for a certain age of development of the child (his puberty).
Phimosis is more common as a congenital pathology, and the causes of phimosis have not yet been precisely established. Several varieties of the manifestation of phimosis make it possible to consider several degrees of this pathology, which differ depending on the physiological manifestation of phimosis and the inconveniences experienced in this case.
The first degree of phimosis is manifested in the exposure of the glans penis at rest, but difficulty in removing it at the time of erection, which is accompanied by pain.
The second degree of phimosis is characterized by difficulties in exposing the glans of the penis both at rest and during erection, sometimes only part of the glans is exposed, which can swell and resemble a bubble.
With the third degree of phimosis, it is almost impossible to bring the head out of the prepuce.
For the fourth degree of phimosis, such a significant narrowing of the foreskin is characteristic , in which it becomes difficult to urinate. In the case of such a development of phimosis, medical intervention is required in early childhood. Signs of phimosis in this case may appear in the form of a too thin stream of urine when urinating, or inflating the preputial bag during urination.
Other symptoms of phimosis that are not related to urinary problems may include:
- Painful phenomena during intercourse;
- Decreased sensitivity of the penis, and, consequently, sexual sensations;
- Decreased potency;
- Premature ejaculation.
Phimosis is not always accompanied by unpleasant sensations, but it is the accompanying inconveniences that make men resort to treatment of this pathology. In addition, asymptomatic phimosis is fraught with a number of troubles. Since there are special glands on the inner surface of the preputium that produce smegma (a complex lubricant that protects the glans penis from drying out, protects the mucous membrane of the penis at the time of intercourse), often with phimosis smegma becomes a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms, which in its the queue gives an impetus to the occurrence of inflammatory diseases such as balanitis, balanoposthitis, as well as oncological diseases both in men themselves (cancer of the penis, papilloma of the glans penis), and diseases in partners (cervical erosion, cervical cancer).
In order to avoid such complications of phimosis, you should pay attention to careful hygiene of the penis: at any opportunity, wash the glans penis and foreskin with soapy water. But since it is impossible to carry out these manipulations with certain types of phimosis (third and fourth degrees), we have to resort to eliminating this pathology.
Phimosis, among other things, can have a complication - "paraphimosis", when the head of the penis slips through the narrowed foreskin, and cannot return to its normal state, then the foreskin clamps the head so tightly (infringes on it) that the blood circulation of the latter is disrupted and the head swelling develops, which even more causes pressure on her. Paraphimosis can result from intercourse or masturbation with phimosis. External signs of paraphimosis are manifested by blueness of the glans penis and its edema. All this is accompanied by acute painful sensations.
First aid for paraphimosis can be provided in a medical facility, where the head is adjusted or the foreskin ring is cut.
Phimosis is treated with anesthetics. Although conservative treatment of phimosis exists along with surgical treatment , it cannot always get rid of the problem, since it is not possible in practice to mechanically stretch the foreskin to the required size and fix these sizes. The use of softening ointments for the foreskin or devices for stretching it does not essentially give a permanent desired effect, but only delays the time of the operation.
Methods of surgical removal of phimosis have proven themselves well, the choice of which is correlated with the complexity of the pathology. Usually, surgery is performed under local anesthesia, general anesthesia is used only in exceptional cases (the patient's small age, personal desire, intolerance to local anesthetics).
Surgical treatment is carried out within one day and does not require inpatient treatment. After two weeks, the patient can already have sex.
Surgical interventions for phimosis are of several directions:
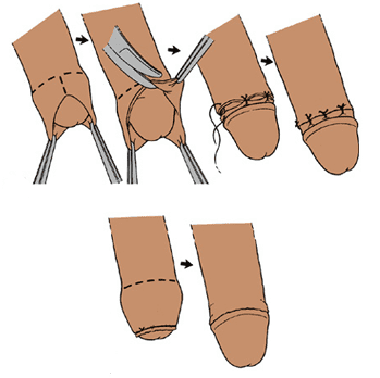
- Excision of the foreskin (in the people - circumcision) provides one hundred percent success in the treatment of phimosis, but has a drawback - the loss of useful functions performed by the foreskin. Sometimes this kind of operation is the only way to get rid of chronic balanitis, balanoposthitis, paraphimosis or fourth degree phimosis.
- Prepucioplasty is an alternative solution to the problem of phimosis, when not all of the foreskin is excised, but only part of it with restoration of functions.
- The Schloffer method is another alternative to circumcision, when the foreskin is not cut off, but cut in such a way that, with a certain stitching, it becomes possible to expand the foreskin ring while preserving the latter. This reshaping of the foreskin has its drawback - healing takes much longer, there may be relapses. There are certain contraindications for this kind of surgery (cicatricial phimosis).
- Laser treatment for phimosis consists in using a laser beam instead of a scalpel. The advantage of this method is its bloodless conduct, since the laser, cutting tissue, simultaneously cauterizes them. A shorter recovery period, minimal pain syndrome and no risk of wound infection can also be attributed to the advantages of laser treatment.

Read

Read



























