Musculoskeletal system >>>> How to treat a hernia of the lumbar spine?
How to treat a hernia of the lumbar spine?
A hernia of the lumbar spine occurs due to a rupture of the intervertebral cartilage (disc), which shifts to the side, protrudes and ceases to fulfill its responsibilities for amortization when pressure is applied to the vertebrae.
Signs of a hernia of the lumbar spine:
- Poorly tolerated pain when walking;
- The pain can radiate to the buttocks, thighs, knees, ankles, toes;
- Numbness in varying degrees of the lower extremities;
- Stiffness in the lumbar spine;
- Violation of reflexes;
- Violation of urination;
- Violation of potency.
A rupture of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar spine can be triggered by a number of factors:
- Overload of the spine when lifting and carrying weights;
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine;
- Accidental injuries (whiplash injury - a sharp bend forward and then backward);
- Long sitting position;
- Excessive body weight.
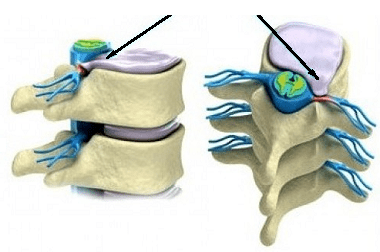
There are two ways to treat a hernia of the lumbar spine: conservative and surgical. The doctor, choosing the way of treatment of a hernia of the spine, carefully examines each case and offers the patient the appropriate treatment methods.
The conservative method of treatment involves the removal of pain syndrome with the help of painkillers and muscle relaxants, individual selection of therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscular corset of the lumbar spine, changing the lifestyle from predominantly sitting to mobile, physiotherapy, massage (only in special cases, so as not to aggravate the traumatic position of the vertebrae and a torn disc), wearing special corsets.
When making a diagnosis - "hernia of the lumbar spine", it is necessary to avoid sharp forward bends, turns around the axis in different directions, lifting and carrying weights in front of you. All these movements can exacerbate the traumatic and painful condition and provoke a worsening of the situation with the injured spine.
Surgical treatment is an extreme measure in the treatment of a hernia of the lumbar spine, when all conservative methods do not help, but can worsen the patient's condition.
Surgical treatment (neurosurgical intervention) can be performed by discectomy, microdiscectomy with a microscope through a small incision, microdiscectomy with an endoscope (contraindicated), percutaneous nucleoplasty (with a needle), by laser vaporization (using electromagnetic radiation that evaporates part of the cartilaginous tissue disc, reducing pressure on nerve fibers).
Microdiscectomy, percutaneous nucleoplasty, laser vaporization have low trauma and allow you to quickly get back on your feet, and after a short period of time, start performing small and metered physical activities. After the restoration of working capacity, supportive physiotherapy, restoration of sensitivity and therapeutic exercises are carried out.

Read

Read



























