Musculoskeletal system >>>> Muscle contracture
Muscle contracture.
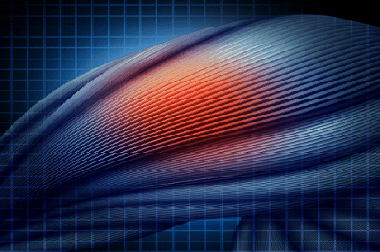
Muscle contracture (myogenic contracture) is a condition of muscle tissue associated with muscle shortening and a decrease in muscle extensibility as a result of trauma, inflammation, degenerative changes, damage to nerve fibers or a sharp reflex contraction when muscle fibers are irritated (thermal, chemical, mechanical). Muscle contracture of any complexity is accompanied by strong painful sensations, which do not make it possible to forcibly stretch the affected muscle and bring it to normal working condition. It is the pain symptom that occurs in muscle tissue during movement that is a sign of contracture.
Contractures can occur in skeletal muscles, muscles of the face, neck, and chewing muscles. Contractures of the muscles of the limbs disrupt flexion-extensor functions, leaving the limbs in a state of incomplete flexion or incomplete extension. Contractions of the masticatory muscles interfere with the movement of the lower jaw, limiting the ability to open the mouth. Contractures of the muscles of the face or neck can cause facial asymmetry and abnormal tilting of the head and neck. Contractures of skeletal muscles can cause distortions and asymmetries of certain areas of the body, limit the body tilts in different directions.
Treating muscle contractures depends on the place of occurrence of contracture, the reasons for its occurrence, the degree of complexity of the disease that caused the muscle contracture. Treatment is aimed at relieving inflammatory processes in muscle tissue by using anti-inflammatory (hormonal and non-hormonal) and painkillers and physiotherapy procedures (dry heat - heating pad, salt; electrophoresis; UHF; Bernard currents), preventing muscle atrophy resulting from muscle immobility by conducting a set of exercises aimed at gradual forced stretching of the affected muscles. Of great importance in the elimination of contractures of any localization is a slow passive movement in the area of the contracture that has arisen and the duration of the contracture existence. The longer the muscle remains motionless as a result of the development of contracture, the more difficult it is to overcome the contracture. Stretch the muscle, having previously relaxed it (for example, by warming up). Stretching a muscle, overcoming unbearable pain, is not recommended, since pain syndrome causes tension in the muscle tissue, resistance and complicates its stretching.
If it is impossible to restore muscle performance by conservative methods, they resort to surgical intervention - myotenolysis, fibrotomy.

Read

Read



























