Musculoskeletal system >>>> Cervical osteochondrosis - causes and prevention
Cervical osteochondrosis - causes and prevention.
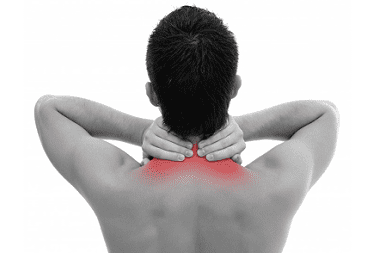
The cervical spine is the most mobile of all the spine. He is loaded 24 hours a day, keeping his head in an upright position of the body, in turns and tilts of the head. Osteochondrosis in the cervical spine develops as a result of compression, deformation and degenerative disorders in the intervertebral discs.
Disorders in the intervertebral structures are caused by impaired blood flow and nutrition of the cartilaginous tissue of the discs, which leads to their thinning and softening. With a changed consistency of cartilaginous tissue, it is easy to injure it, for example, by an unsuccessful (sharp) turn of the head, prolonged states of tilt of the head, when the muscle tissues are stretched unevenly.
The reasons for the development of cervical ostechondrosis:
- Untrained neck muscles,
- Complication after injury (for example, prolapse of the cervical vertebra or sprain in an accident),
- Compression of the cervical spine,
- Calcification of bones and tissues of the cervical spine,
- Systemic diseases of the articular joints (including vertebrates),
- Sedentary forced head position.
Osteochondrosis of the neck is one of the most dangerous painful conditions of the body.
The vertebral artery and many nerve fibers run along the spinal column in the neck. Compression of the vessel supplying blood to the brain will inevitably cause oxygen starvation, a violation of the trophism of brain tissue, which will lead to dizziness, headaches, impaired coordination, visual impairment, hearing impairment and may result in a stroke. Compression of nerve endings in the cervical region disrupts the pathways of innervation of the brain, cervical and thoracic regions. This will be reflected in the numbness of the tissues of the head, neck, upper extremities. It can lead to a deterioration in mental abilities, impaired functioning of the vestibular apparatus, impaired tactile sensations.
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Pain syndrome in the cervical spine,
- When you turn your head, a crunch is heard,
- Numbness of the scalp, hands,
- Tingling in the hands,
- Headache,
- Dizziness, darkening of the eyes,
- A feeling of being stunned may develop,
- Sound effects in the ears are possible.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis involves lifestyle changes, in particular:
- The transition from sedentary work and passive rest to active physical education,
- Particular emphasis is placed on training the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck,
- Breaks during sedentary work every hour (half an hour) to warm up the neck muscles,
- Posture correction,
- Swimming and sports that promote body stretching (volleyball, basketball), exclusion from the diet of foods that promote salt formation and salt deposition with the body's tendency to such metabolic disorders.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is a complex process that requires an integrated approach: a combination of massage, physical exercises for the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle, drug therapy and physiotherapy.
Swimming helps well with osteochondrosis of the neck. Exercise should use the muscles of the neck: tilting the head in different directions and back, turning the head (perform very carefully at a slow pace), stretching the head up. Raising dumbbells with outstretched arms at a slow pace strengthens the neck muscles. The massage is carried out very gently, by pressing on the muscles of the neck. Posture correction is performed.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is represented by shock wave therapy (SWT), which allows the destruction of osteophytes - bone growths on the vertebrae. It is carried out in several sessions. SWT is an alternative to surgical excision of osteophytes (in severe cases).
Drug therapy is represented by anti-inflammatory, analgesic, vasodilator drugs and muscle relaxants. It is not recommended to use medications without a doctor's recommendation, since they all have side effects that must be correlated with the general state of health and a history of diseases.

Read

Read



























