Parasitic diseases >>>> Echinococcus - why is it dangerous?
Echinococcus - why is it dangerous?
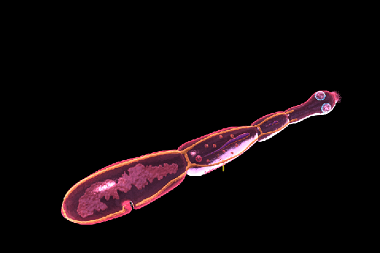
Echinococcus - tapeworm - a parasite, a relative of the bovine tapeworm, but different from it in size, which can reach 0.2 inch.
Echinococcus larvae withstand ambient temperatures in Celsius from minus (-30) to plus (+40). Echinococcus eggs survive in the external environment for up to 1.5 months and are resistant to desiccation.
Echinococcus eggs are spread into the environment through the feces of infected animals (sheep, pigs, dogs, etc.). Eggs with dried fecal dust are carried by winds over long distances and settle on the surface of the earth, plants and enter water bodies.
A person becomes infected through eating poorly washed or thermally unprocessed agricultural products or through direct contact with a sick animal, violating the rules of personal hygiene.
If animals are an intermediate host of echinococcus, then a person becomes its final owner, where echinococcus has many opportunities for the location of its capsules (cysts) and reproduction of offspring.
Cysts affect various organs, grow in size and gradually turn the organ into non-functional and destroyed by necrosis. As the cysts grow (and echinococcus has a very slow development), substances that have an allergic effect on the human body are released outside of them.
Such allergic reactions can occur at an accelerated or slowed down rate, in connection with which a person can develop not just an allergic reaction, but its extreme manifestations: Quincke edema and anaphylactic shock. It is these allergic effects of echinococcus on the human body that make it deadly in the body.
Signs of echinococcosis:
- general malaise with vague symptoms,
- allergic rashes of unknown origin,
- signs of body intoxication (headache, nausea),
depending on the organ of the lesion, the symptoms may also differ, which resemble the diseases typical for this organ:
- with liver damage (the most common cases of echinococcosis), there is pain in the liver, heaviness, nausea;
- with lung damage, the symptoms of echinococcosis resemble bronchitis, pneumonia and other pulmonary diseases;
- with damage to the heart bag, there are failures in cardiac activity;
- the location of the echinococcal whale in the brain is fraught with disorders of the central nervous system.
To identify echinococcus in the body, X-ray, MRI, ultrasound are used, a blood test is performed for the presence of antibodies to echinococcus.
Treatment of echinococcosis can be conservative (antiparasitic agents) or surgical (in the presence of large cysts on vital organs). Surgical intervention is very difficult, since echinococcus cysts can be located in dangerous places of the organ, and their removal is associated with little recoverable or irreparable damage to the organ.
Prevention of echinococcosis is a careful attention to personal hygiene, and the rules for processing food before eating. You should not drink water from open sources, take food for food with dirty hands, hug or kiss street animals, even if these are animals you know well.
The effectiveness of the treatment of echinococcosis depends on the early detection of the parasite in the human body and its timely destruction.

Read

Read



























