Infectious diseases >>>> Foot and mouth disease - what is it?
Foot and mouth disease - what is it?
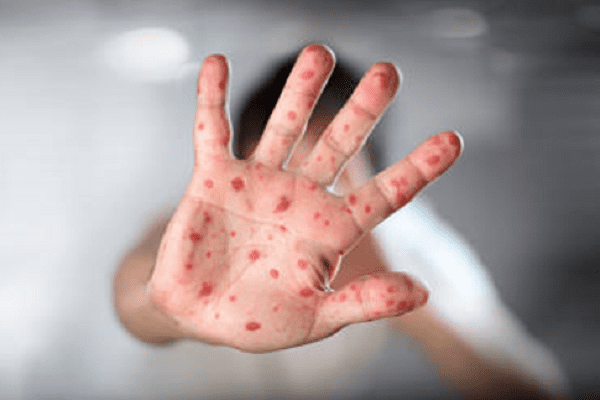
Foot and mouth disease (FMD disease) is a viral disease caused by the Aphtovirus virus. Ungulates are carriers of the virus. The virus is transmitted by contact, and the risk group includes workers at stud farms and livestock farms.
The foot and mouth disease virus is viable in external environments, but when heated or irradiated, when treated with disinfectants and alkalis, it dies. A person who is infected with foot and mouth disease does not pose a threat to other people.
Signs of Foot and Mouth disease:
- inflammatory processes develop on the mucous membrane and skin (usually visible changes are observed on the mucous membranes of the mouth, urethra),
- changes on the skin most often develop in the area of the limbs, face,
- the mucous membrane and skin swells,
- bubbles and erosive foci develop,
- there is a burning sensation, usually inflammation can be observed in the conjunctival region,
- sometimes (more often in children) dyspeptic disorders (bowel disorders, stool disorders) appear,
- the disease has an acute onset: high fever, chills, aching limbs and lower back, headache develops.
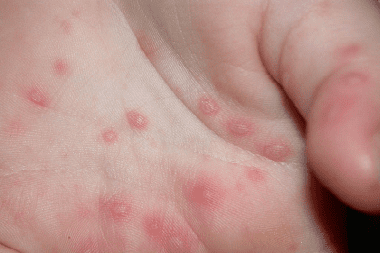
Treatment of Foot and Mouth disease is carried out in a hospital. Supportive therapy is applied, antiviral and healing ointments are applied locally to the foci of tissue damage. In fact, the immune system fights the virus, and medicine requires supportive and restorative therapy. With severe damage to the oral cavity, patients have difficulty eating. In such cases, prescribe liquid food or parenteral administration through a tube.
Foot and mouth disease is a curable disease. Deaths are possible only in infancy, weakened age or in old age with poor body resistance.

Read

Read



























