Oncology >>>> Lipoma
Lipoma.
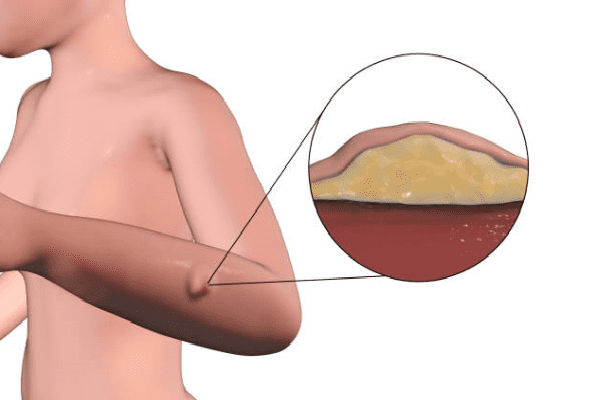
Lipoma (synonym: lipoblastoma, in everyday life is called "wen") is a tumor that develops from the cells of adipose tissue. Since the layer of adipose tissue is formed in many places of the human body, the locations of the lipoma are quite diverse: these are subcutaneous, intermuscular, retroperitoneal spaces, breast tissue, gastrointestinal tract, tissues of internal organs (kidneys, liver, adrenal glands, uterus, etc.) Although a lipoma is not considered a malignant neoplasm, it is prone to relapse after removal, and sometimes to malignancy (malignancy).
According to its structure, a lipoma is an accumulation of fat cells united in lobules and enclosed in a capsule of connective tissue. Each of the lipoma lobules is separated from the neighboring stroma, and depending on how much the lipoma tissue is covered with stroma, the consistency of the tumor itself also depends. In this regard, lipoma is classified as:
- Lipofibroma - its basis is predominantly adipose tissue,
- Fibrolipoma - its basis is mainly connective fibrous fibers,
- Myolipoma - it contains smooth muscle fibers,
- Angiolipoma - along with adipose tissue also contains blood vessels,
- Myelolipoma is a combination of adipose tissue and hematopoietic tissue.
The lipoma itself is not painful, but its growth sometimes squeezes the nerve endings on the adjacent organs, which causes painful sensations.
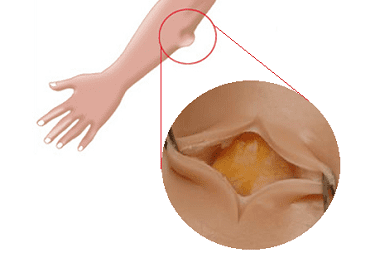
Lipoma is easy to diagnose, since it is visible to the naked eye (subcutaneous), and also, in the case when the lipoma is located intermuscularly, behind the peritoneum or on internal organs, it is clearly visible on the radiograph.
The true causes of lipoma are still vague. But there are several assumptions about the factors contributing to its occurrence:
- Fat cells, atypical for humans, retained in tissues during the development of the embryo;
- Disruption of metabolic processes;
- Endocrine Disorders.
Lipoma can only be treated surgically, but it is not shown in all cases, only when its rapid growth and / or impressive size causes serious damage to neighboring tissues and organs (for example: infringement of nerve fibers, dysfunction of organs when they are squeezed, distortion of appearance). For a long time, a lipoma may not change in size or grow very slowly, but cases have been described when trauma to a lipoma causes its malignancy and acquires the properties of a liposarcoma.
There are three ways to remove a lipoma:
- cardinal removal of the lipoma together with the capsule (advantages - no relapses, disadvantages - cosmetic defect),
- endoscopic removal of a lipoma with its preliminary destruction inside the capsule (advantages - inconspicuous incision, disadvantages - relapses are possible),
- liposuction of lipoma (advantages - good cosmetic result, disadvantages - incomplete removal of lipoma tissues, which provokes relapses).
Treatment of lipoma with folk remedies will not bring any results, since the development cycle of a lipoma is independent and does not depend on an increase in the amount of adipose tissue or its decrease.

Read

Read



























