Gynecology and Mammology >>>> Causes of mastopathy - what you need to know. Part 1
Causes of mastopathy - what you need to know. Part 1.

Mastopathy refers to a number of diseases of the mammary glands (MF) of a non-oncological nature. It is associated with pathological changes in tissues, the so-called proliferation (growths) and regressive changes that disrupt the relationship between the connective and glandular structure of the breast. Mastopathy is a polyetiological (multifactorial) disease associated with environmental factors, hormonal disorders and a genetic component. At the moment, not a single specific factor has been found, about which it could be said with confidence that it is he who is a risk factor for the occurrence of this disease. But there are a number of reasons leading to the onset of mastopathy.
Etiology (reasons).
All reasons can be roughly divided into main and accompanying development of mastopathy.
Basic:
- a hereditary factor that is responsible for the development of benign and (or) malignant diseases in maternal women;
- disturbances in the hypothalamic-pituitary system (neuroendocrine disorders);
- pathological functioning of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) increases the risk of mastopathy by about 4 times;
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract contribute to the overall risk picture, since the liver plays an important role in the metabolism of excess endogenous estrogens and their utilization;
- disruption of the adrenal glands;
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries ( chronic salpingo-oophoritis : as a result of which the production of sex hormones is disrupted);
- inflammatory diseases of the mammary glands ( mastitis ).
Causes of mastopathy:
- stress , neurosis, depression;
- obesity in combination with arterial hypertension (high blood pressure) and diabetes;
- lack of iodine can lead to an imbalance in the mechanism of interaction between the hypothalamus and the mammary gland;
- irregular sex life leading to violations of the hormonal status of a woman;
- high background radiation;
- trauma and microtrauma;
- artificial termination of pregnancy abruptly stops proliferative processes in the mammary gland, and the process of regressive changes in the tissues occurs unevenly, while disrupting the tissue structure of the mammary glands;
- no pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Pathogenesis (Mechanism of development)
The mammary gland (MF) has a complex structure. It is structurally formed by glandular tissue (parenchyma), connective tissue (stroma) and adipose tissue, which are in a certain ratio, which depends on the physiological state of the body at a certain period. The breast contains receptors that are sensitive to about 15 different types of hormones. During a woman's life, the mammary gland experiences continuous hormonal "bombardment", which leads to cyclical changes in its structure and functioning, depending on the level of sex and gonadotropic hormones.
To a greater or lesser extent, all components of the breast are subject to hormonal effects. First of all, this is the parenchyma (glandular tissue), which is influenced by estrogens and progesterone (produced by the ovaries and partly by the adrenal glands), prolactin and growth hormone (produced by the anterior pituitary gland). And during pregnancy, the action of placental hormones ( estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, lactogen), produced by the placenta itself. The stroma (connective tissue) is also subject to hormonal "bombardment" by estrogens, which provokes hyperplasia of this tissue component. As for adipose tissue (or rather its adipocytes), it itself serves as a depot of estrogens, formed as a result of the reaction of aromatization of androgens into estrogens (estradiol and estrone) in adipose tissue. Adipocytes of adipose tissue do not synthesize sex hormones themselves, but capture them from plasma.
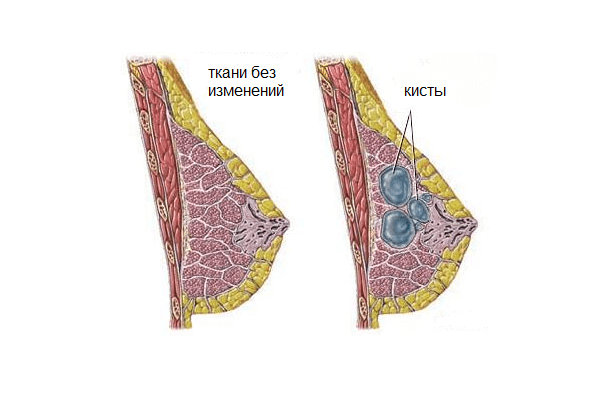
The morphophysiological features of the functioning of the breast are such that estrogens and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle and directly affect the breast tissue. Proliferative processes in the mammary gland occur under the influence of estrogens (cells multiply). Progesterone limits the effects of estrogens, while inhibiting proliferation processes. Under the influence of various unfavorable situations, an imbalance in the amount of hormones occurs - a lack of progesterone and an excess of estrogen, which leads to excessive uncontrolled proliferation of breast tissue. Over time, this proliferation turns out to be a factor in the formation of cystic cavities.
Mastopathy develops against the background of hormonal imbalance, the result of which is a violation in the ratio of progesterone and estrogen, as well as increased secretion of prolactin. In a normal situation, prolactin is produced in significant quantities during pregnancy, or during lactation in order to form breast milk. But pathological processes in the work of the pituitary gland can lead to the fact that an excess of prolactin is formed outside of pregnancy. In turn, adrenal hormones (corticosterone, aldosterone, deoxycorticosterone) affect the breast tissue, increasing the sensitivity of receptors to prolactin and thereby stimulating the proliferation of epithelial cells and changes in the structure of the ducts. With a tendency to increase prolactin, the development of fibrous changes in the breast tissue is observed.
An important role is assigned to the hormones of the pancreas, which are involved in the regulation of the processes occurring in the mammary gland. So insulin, along with progesterone, prolactin and corticosteroids, takes part in the development of ducts in the mammary glands.
At the same time, hormones produced by the thyroid gland have a special effect on the development and functionality of epithelial cells in the mammary gland, and also affect the metabolism and synthesis of steroid hormones in the ovaries.
Diseases of the liver and biliary tract disrupt the inactivation of steroid hormones, inhibiting the utilization of estrogens and thereby increasing their concentration in the body.
Gonadotropic hormones (pituitary hormones) also have a great effect on the formation of breast tissue. So their deficiency leads to hypoplasia of the mammary gland (sometimes to asymmetry), and an overabundance leads to the development of fibrous tissue.
Thus, the correct study and diagnosis of the hormonal status of a woman is necessary for the prevention and treatment of pathological changes in the glands that occur during life.

Read

Read



























