Otolaryngology >>>> Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis.
The term "chronic tonsillitis" refers to chronic inflammation of the tissue of the palatine tonsils. The prerequisites for the onset of tonsillitis are the features of the anatomical and cellular structure of the tonsils. The palatine tonsils are part of the immune system, they are part of the so-called lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring, perform a barrier function when an infection enters the oral cavity, as if "taking fire on themselves." Unlike other structures, the palatine tonsils have a kind of cleft (lacunae) that penetrate the body of the amygdala, forming a network. As a result of chronic inflammatory processes, lacunae are covered with scar tissue, which disrupts their natural drainage, and this, in turn, creates ideal conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
Exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis usually occur two or three times a year. This is facilitated by unstable weather conditions with temperature drops. Since the tissue of the amygdala is permeated with a network of nerve endings, it is sensitive to changes in the environment. Hypothermia can be the impetus for the development of the process. And also the periods of inflammation can coincide with the height of a viral infection or the ingress of pathogenic bacteria from the outside.
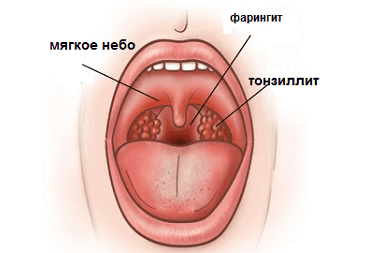
Signs of chronic tonsillitis.
Lymphocytes, which are the bulk of the amygdala parenchyma, themselves are inflammatory cells, therefore it is histologically difficult to distinguish between inflamed amygdala tissue from healthy tissue. It is believed that the precursors of chronic tonsillitis are a history of frequent tonsillitis (history of the disease).
The size of the amygdala does not indicate inflammation, but the loose appearance of the amygdala is a cause for concern.
Round yellowish formations begin to shine through the outer layer of the tonsil - these are suppurating follicles that contain decaying lymphocytes and necrotic tissue.
In the lacunae of the tonsils, liquid purulent contents are visible, which, when pressed lightly, are squeezed out.
Sometimes an unpleasant odor occurs.
Feeling the enlarged lymph nodes located in the corner of the lower jaw and cervical spine also gives reason to believe that there is inflammation.
A patient with chronic tonsillitis complains of sore throat, difficulty and pain when swallowing, sore throat, fever up to subfebrile - 37 - 37.5 in Celsius (but the disease can proceed without fever).
Not all signs of chronic tonsillitis are simultaneously manifested in every patient, it sometimes happens that no signs are observed.
Chronic tonsillitis is dangerous because it leads to complications - rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, acute or chronic glomerulonephritis.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis is divided into two methods: conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment is chosen when there is a contraindication for surgical intervention or when frequent exacerbations of the disease pose a threat of complications.
Tonsils are washed with antiseptic solutions (you can use phytonastoes of antiseptic action), treated with trypsin solution, remove necrotic plaque, purulent "plugs", lubricated with Lugol's solution or use an aerosol containing Lugol . You can rinse with a solution of bacteriophages at room temperature or warm the bottle in your hands. Physiotherapy is carried out: ultraviolet irradiation using a tube, electrophoresis, low-frequency helium - a neon laser. Physiotherapeutic treatment of tonsillitis is contraindicated in cases of suspicion or in the presence of cancer.
Surgical treatment for chronic tonsillitis is a radical treatment. It means the removal of the tonsils with the adjacent connective tissue. The procedure is called tonsillectomy . The operation is performed most often under local anesthesia. Healing occurs quickly enough (two weeks).

Read

Read



























