Cardiovascular system >>>> The mechanism of blood clots and the causes of thromboembolism
The mechanism of blood clots and the causes of thromboembolism.
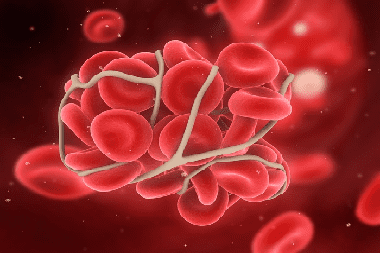
The mechanism of thrombus formation was created by nature itself to "repair" damaged blood vessels. The process of thrombus formation is called thrombosis. The meaning of this process is to carry out irreversible denaturation of proteins and blood cells (platelets and erythrocytes) in order to seal the injury site. A distinctive feature of blood clots is the fact that they attach to the wall of a blood vessel, have a layered crumbling structure and a rough surface. The entire structure of a thrombus is designed to maintain blood flow, and its strong adhesion to the vessel under normal conditions does not provide for its separation.
The mechanism of blood clot formation.
When a blood vessel is damaged, substances that inhibit antiaggregation processes (that is, processes that prevent blood coagulation) in this place of the bloodstream begin to be released from its wall. In this case, platelets begin to change and disintegrate, and procoagulants (thrombin and thromboplastin) are released into the blood - substances that promote blood clotting. Under the action of thrombin, febrinogen (a protein that affects the erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is converted into fibrin, which in the form of a mesh of threads forms the basis of a thrombus. In the cells of this network, blood cells are collected: aggregated platelets, leukocytes and erythrocytes. The structure thickens over time. The thrombus formation process is over and the "leak" of blood is eliminated.
The causes of thrombus formation can be varied.
- Physical damage to the walls of blood vessels - mechanical injury, electrical injury;
- Chemical damage to the vascular walls;
- Exposure to microorganism endotoxins;
- Large-scale surgical interventions;
- Childbirth;
- Physiological disorders - atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, allergies;
- The release of adrenaline inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandin (prostaglandin slows down blood clotting), thereby promoting thrombus formation;
- Violations of the system that inhibits blood coagulation, as well as disorders of the system that catalyzes blood clotting;
- Taking hormonal drugs (for example, contraceptives);
- Smoking promotes the formation of thromboxane under the influence of nicotine - a powerful regulator of blood clotting;
- .The process of the onset of neoplasms (the development of benign and malignant tumors) promotes thrombus formation;
- A sedentary lifestyle contributes to poor circulation and can cause pulmonary embolism or venous thrombosis.
Consequences of thrombus formation.
An uncontrolled process of thrombus formation is the cause of the development of many diseases:
- Ischemia of the heart
- Ischemic brain stroke
- hrombophlebitis development
- Limb gangrene
- Vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis
- Slow blood flow
- Violations of blood rheology (quality characteristics of blood)
Factors contributing to the detachment of a blood clot from the vessel wall.
Violation of the elastic properties of blood vessels leads to the development of their fragility, which means that the vessel wall will not be able to hold the blood clot firmly enough. There may be a violation of the integrity of the vascular wall at the site of attachment of the thrombus.
Since the thrombus is constantly washed by the blood and, being held on the wall of the vessel, experiences continuous resistance to the blood flow, the quality characteristics of the blood, which exert pressure on the thrombus - the fluidity and viscosity of the blood, are of particular importance. The higher the fluidity of the blood, the easier it is for it to wash the thrombus, bending around it. The higher the viscosity of the blood, the more difficult it is for the blood clot to withstand the blood pressure in the vessel.
There is such a concept - "floating" thrombus . Such a thrombus is connected to the vessel wall pointwise and constantly sways in the blood stream. Any sudden movement: coughing, taking a deep breath, laughing, muscle tension when lifting weights can rip him off the spot and throw him into the blood stream. There are special hardware research methods to find out which blood clot can be dangerous - coagulogram, ultrasound angiology, sonoelastography.
The result of the separation of a blood clot from the vessel is embolism - blockage of the vessel lumen. If a small vessel is clogged, then in the worst case it will end in gangrene of the limb, in the blood vessel of which thromboembolism has occurred , but if the blood vessel that supplies blood to the heart or brain is clogged, then the end result will be necrosis and death of the whole organism.

Read

Read



























