Endocrinology >>>> Insulinoma - signs and treatment
Insulinoma - signs and treatment.
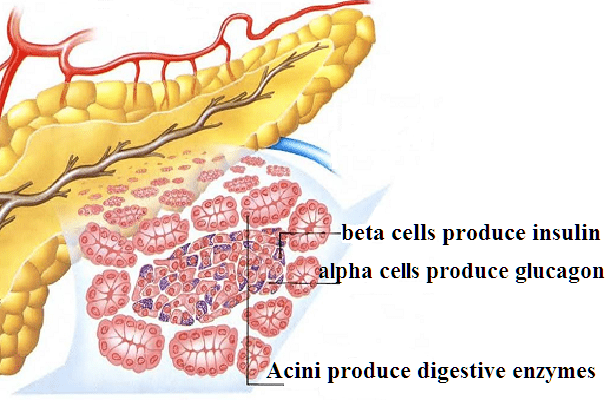
The human pancreas contains, in the form of inclusions, clusters of cells responsible for the production of the hormone insulin (beta cells). A scattering of such inclusions is located in the pancreas in varying concentrations and is called Largenhans islets. Due to some circumstances, part of the cells of the islets of Largenhans begins to uncontrollably secrete excess insulin, which leads to the development of hypoglycemia. An accumulation of beta cells that abnormally produce insulin is called insulinoma.
According to statistics, among benign hormonally active neoplasms, insulinoma is about 75% and affects people of different ages (from infants to old age). The size of insulinomas can range from a few millimeters to 15 centimeters, but most often insulinomas are found in clinical practice of about two centimeters. Despite the fact that insulinoma is a benign tumor, there are known cases of malignancy and metastasis to nearby internal organs, mainly to the liver.
Typical signs of insulinoma (Whipple triad):
- Attacks of hypoglycemia on an empty stomach (for example, in the morning or during long breaks between meals),
- A sharp decrease in blood sugar levels during an attack of hypoglycemia,
- Relieve a seizure quickly with intravenous glucose or high-sugar foods.
In addition to the above symptoms of insulinoma, there are signs of psycho - motor excitement during hypoglycemia; incoherent speech; uncontrolled emotional outbursts of aggression, anger, anger, fun, euphoria; disturbances of consciousness up to distortion of perception of the surrounding reality, hallucinatory phenomena. With insulinoma, there may be an increase in appetite and a gain in excess weight associated with this phenomenon, but in some cases the opposite reaction may develop - loss of appetite, up to an aversion to food, followed by weight loss. With the latent form of the course of hypoglycemic disease (synonymous with insulinoma), dizziness, headaches, memory impairment, apathy, muscle weakness, impaired reflexes, nystagmus may occur.
Diagnosis of the presence of insulinoma is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of professionals. In order to diagnose the patient, fasting is recommended for a day, then a blood test is performed, and low blood glucose levels are detected, but unjustifiably high insulin levels, which confirms the diagnosis of "insulinoma".
Insulinoma treatment is accompanied by surgery to excision of the tumor or resection of the pancreas, depending on the size and location of the tumor. In case of malignancy, insulinomas are treated with chemotherapy.

Read

Read



























