Urology >>>> Hydronephrosis - signs and treatment
Hydronephrosis - signs and treatment.
An increase in the volume of the renal pelvis and calyces due to obstructed outflow of urine from the kidney leads to hydronephrosis. Such changes in the size of the pelvis and calyces are associated with the processes of atrophy of the parenchymal tissue of the kidney.
The causes of hydronephrosis lie in various external and internal factors: obstruction of the urinary tract, obstructions in the path of the urinary tract (tumors, blood clots, polyps, bladder diverticula, malfunctioning of the bladder valves, stones, etc.)
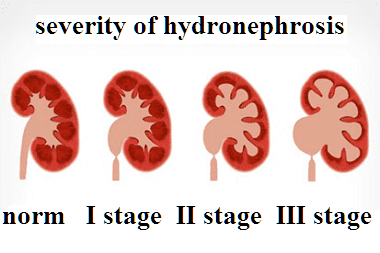
Hydronephrosis often develops in women 20-60 years old with gynecological problems of an oncological nature or due to the state of pregnancy. Hydronephrosis in men often develops after 60 years with prostate cancer or prostate adenoma.
Signs of hydronephrosis depend on the rate of obstruction of the renal segments:
- In the acute form of the course of hydronephrosis, attacks appear similar to attacks of renal colic in the lumbar region. Pain can spread along the ureter, radiate to the groin, to the thigh. The urge to urinate, accompanied by soreness, increases. Nausea, urge to vomit may develop. In the urine with hydronephrosis, blood is visually determined (gross hematuria). Or blood is detected in laboratory tests (microhematuria).
- Chronic hydronephrosis may not manifest itself with obvious symptoms for a long time, except for discomfort in the lumbosacral region with excessive fluid intake or physical overload. Against the background of chronic hydronephrosis, hypertension can develop; if an infection enters the urinary system, hydronephrosis can be complicated by purulent pyelonephritis. Untreated chronic hydronephrosis can have a complication - renal failure or rupture of the hydronephrotic sac with the outflow of contents into the retroperitoneal space.
Treatment of hydronephrosis involves surgical intervention of various levels of complexity. In an emergency, a nephrostomy is performed (percutaneous puncture of the renal pelvis to create a pathway for urine outflow and reduce pressure in the kidney). For urinary tract strictures, bougienage, balloon dilation, or stenting are performed. With urolithiasis, lithotripsy (crushing stones) is performed.

Read

Read



























