Otolaryngology >>>> What is sinusitis?
What is sinusitis?

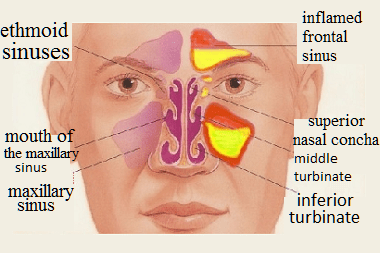
Four paranasal sinuses border and communicate with the nasal cavity: maxillary (paired), frontal (paired, but there may be one or none at all), ethmoid cells, sphenoid (divided by a septum into two parts). Inflammatory processes often occur in the paranasal sinuses, which have a common name - sinusitis. Depending on which of the sinuses the inflammatory process develops in, sinusitis is given a specific name. Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is called sinusitis; inflammation of the frontal sinus is called frontal sinusitis; the inflammatory process occurring in the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth is called ethmoiditis, and the inflammation in the sphenoid sinus is called sphenoiditis. When all the sinuses are involved in the process of inflammation, the disease is given a name - pansinusitis. If the inflammation occurs in the sinuses located on only one side, then the disease is called hemisinusitis.
According to the nature of the inflammatory process, sinusitis is divided into:
- Catarrhal, in which there is nasal congestion, bursting, pressing pain in the sinuses, headache;
- Purulent, when the above symptoms are supplemented by purulent discharge and fever;
- Allergic, when as a result of allergic edema of the nasal mucosa, the mucous secretion enters the nasal sinuses;
- Polypous, when, against the background of a prolonged inflammatory process, a pathological proliferation of connective tissue in the sinuses occurs.
As a rule, sinusitis occurs against the background of other diseases, or is a complication of any disease associated with infection of the mucous pathogenic microflora. Sometimes the inflammatory process in the maxillary paranasal sinus can be combined with the pathology of the upper jaw, since they are anatomically related. This disease has its own name - odontogenic sinusitis , and requires additional specific methods of research and treatment. But it often happens that sinusitis also develops as an independent disease, for example, as a result of an injury to the nose (face) or hypothermia.
Signs of inflammation in sinusitis:
- The mucous membrane of the paranasal sinus swells,
- The mucous membrane of the sinus is hyperemic,
- The mucous membrane thickens approximately twenty times,
- The lumen of the sinus is narrowed and the outflow of mucous secretion is difficult,
- The headache gets worse
- The sense of smell is impaired
- There may be a smell from the nose,
- Difficulty or no nasal breathing,
- The general state of health worsens.
In acute inflammation, edema of the mucous membrane causes compression of the blood vessels, which in turn leads to the development of purulent processes. Chronic purulent processes cause thickening of the sinus mucosa, hyperplasia and fibrosis. This is how polyps and cysts arise.
Complications of sinusitis provoke disturbances in the respiratory, circulatory, digestive systems and complicate the course of diseases of the respiratory tract and digestive tract.
Sinusitis is responsible for the violation of nasal breathing , which adversely affects the supply of oxygen to the brain, and also leads to disruption of gas exchange in the lungs, complicates the course of diseases such as bronchial asthma.
There are times when sinusitis can cause trigeminal neuralgia (in particular, its second branch). In this case, a person begins to experience a sharp pain comparable to an electric shock. A characteristic symptom of neuralgia of the second branch of the trigeminal nerve is the localization of pain during mimic movements in the area of the nasolabial fold, the wings of the nose, and the upper lip. And if an otolaryngologist is usually involved in the treatment of sinusitis, then in such cases additional consultations of a dentist and a neurologist are necessary.

Read

Read



























