Musculoskeletal system >>>> Osteitis
Osteitis.
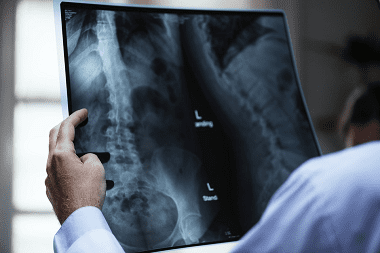
Osteitis is an inflammatory disease of bone tissue, causing its destruction, proliferation, resorption and even necrosis, as the most unfavorable development option.
The causes of osteitis lie in traumatic external influences or in infection by an endogenous or exogenous method.
It is possible to get osteitis as a complication as a result of trauma: bruises, cracks, fractures. infectious agents can penetrate the bone tissue during open trauma or surgery, as well as with the flow of blood or lymph from foci of an existing internal infection (for example, with tuberculosis, syphilis, phlegmon, abscess, and the like).
The signs of osteitis depend on the form in which the disease proceeds: chronic or acute. Chronic osteitis may not designate itself as such until an exacerbation occurs. The factors provoking an exacerbation include colds, hypothermia, recurrence of chronic infections.
Osteitis manifests itself in the form of pain syndrome in the bone region, which may be accompanied by edema or redness, but has the ability to proceed without visible changes. Osteitis can be diagnosed using X-ray; the image shows darkened areas of the bone, occupying a different area (from several mm to several centimeters).
Treatment of osteitis depends on the timely detection of the disease and urgent measures taken. Depending on what factors served as the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process, therapy is also chosen. Infectious origin, osteitis is treated with antimicrobial therapy, immunomodulators. To create an outflow of purulent contents and gain access to the focus of inflammation, drainage systems are installed, which can serve as a channel for the introduction of antibiotics and proteolytic enzymes into the focus of inflammation.
In complicated cases of the course of osteitis, bone tissue resection is performed, that is, segmented removal of the bone material that has undergone destruction.

Read

Read



























