Respiratory system >>>> Atelectasis of the lung
Atelectasis of the lung.
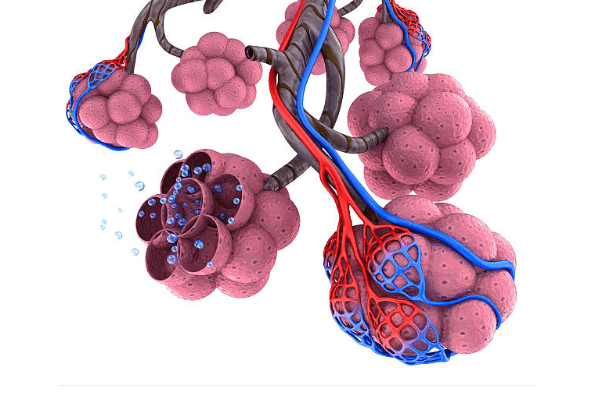
Human lungs consist of many segments - lobules, resembling a pyramid in shape. The bronchus enters the apex of each lobule - the pyramid and branches into bronchioles, at the ends of which there are clusters of alveoli - bubbles filled with oxygen when inhaled. Thus, oxygen is available to each lobule. Initially, the alveoli are in a collapsed state and only at the moment of the first breath at birth they open, making it possible to straighten out the lung tissue.
It sometimes happens that, under certain conditions, the entire lung or its segment is in an unfolded state, which leads to the impossibility of oxygen entering the alveoli, and, therefore, disrupts the breathing process, causing a state of respiratory failure. In these cases, they speak of atelectasis of the lung or atelectasis of the segments of the lung.
Atelectasis are primary - they occur at the time of birth, when during the first inhalation any segment of the lung or the entire lung does not expand; or secondary - occur during life as a result of pathological conditions in the lung tissue in certain diseases (pneumonia, pleurisy, fibrosing alveolitis, tuberculosis, cysts, tumors), lung injuries (compression, surgery), cicatricial changes in the bronchi, fluid accumulation in pneumothorax, spasm of the bronchi, accompanied by the closure of the lumen of the bronchus, aspiration with vomit or foreign bodies.
When atelectasis occurs, it matters how much of the lung volume falls out of the ventilation process, and at what speed this happens. The most dangerous is the rapidly developing atelectasis of the entire lung. When diagnosing atelectasis, the most reliable is an X-ray examination of the state of the lung. With atelectasis of the lung on an X-ray, the entire lung or part of it (lobe or segment) is darkened. Depending on how large-scale atelectasis is, the internal organs adjacent to the changed lung begin to shift towards it. In this case, one half of the chest can be visibly reduced outwardly. When inhaling, the mediastinal organs are displaced towards the affected lung, while exhaling - in the opposite direction.
Signs of atelectasis of the lung or its segment resemble those of pulmonary insufficiency:
- Shortness of breath,
- Cough,
- Cyanosis (blue discoloration) of the skin of the face,
- Rapid pulse,
- Tachycardia,
- Percussion (tapping) produces a dull sound,
- On auscultation (listening), no noise in the lung.
Treatment of atelectasis of the lung is usually carried out in a hospital, and it is aimed primarily at eliminating the factor that provoked atelectasis:
- With atelectasis caused by compression of the lung segments by a tumor or cyst, surgery is indicated;
- With compression atelectasis associated with the accumulation of fluid or air in the pleura, drainage of the pleural cavity is shown;
- Atelectasis caused by a foreign body or fluid entering the bronchi requires bronchoscopy or bronchial catheterization;
- Atelectasis, caused by congestion in the lungs and accumulation of sputum, requires the use of diluents and expectorants, bronchodilators;
- In parallel with drug therapy, massage and special breathing exercises are prescribed, which can also be used as the prevention of atelectasis in pulmonary diseases.

Read

Read



























