Endocrinology >>>> Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia.

Hypercalcemia is a condition of the body characterized by an increase in the content of calcium ions in the blood (that is, calcium in a free state). The onset of hypercalcemia can be said when the concentration of calcium ions is 2.0-2.5 mmol per liter of blood. If tests show an increase in total calcium up to 3.0-3.5 mmol per liter of blood, then this is considered a threatening manifestation of hypercalcemia .
Forms of hypercalcemia:
- Mild: increasing calcium ions up to 2.0 mmol per liter, total calcium up to 3.0 mmol per liter;
- Moderate: increase in calcium ions up to 2.5 mmol per liter, total calcium up to 3.5 mmol per liter;
- Severe: increases in calcium ions in excess of 2.5 mmol per liter, total calcium in excess of 3.5 mmol per liter.
The content of calcium in the blood can be characterized as a constant value, but in the case when the concentration of calcium in the blood exceeds the excretion of calcium in the urine or its content in the bones, then we are talking about true hypercalcemia.
Hypercalcemia reasons:
- Hyperparathyroidism or neoplastic processes that activate bone resorption;
- Paget disease, hyperthyroidism;
- Increased absorption of calcium in combination with hypocalciuria (decreased excretion of calcium in the urine);
- Hypervitaminosis of Vitamin D provokes an increase in intestinal calcium absorption and increases the rate of bone resorption;
- Long-term use of drugs containing lithium;
- Long-term use of thiazide diuretics and theophylline overdose;
- The development of acute and / or chronic adrenal insufficiency increases bone resorption;
- Acute muscle necrosis in combination with acute renal failure releases previously deposited calcium in the muscle;
- Chronic acidosis;
- Hereditary disease - hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, which is characterized by increased reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules;
- Jansen metaphyseal chondrodysplasia is a form of dwarfism caused by mutations in the parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH) and PTH-like peptide gene;
- Breast cancer and extensive bone metastases;
- Congenital lactase deficiency in newborns.
Signs of hypercalcemia occur with moderate to severe hypercalcemia and involve many organ systems:
- Decreased appetite;
- Nausea, urge to vomit;
- Constipation;
- Development of gastric ulcer and intestinal ulcer;
- Increased blood pressure and sometimes asystole symptoms;
- Dehydration;
- Renal dysfunction (polyuria, decreased glomerular filtration);
- Bone and joint pain,
- Weakness;
- Lethargy;
- Depression.
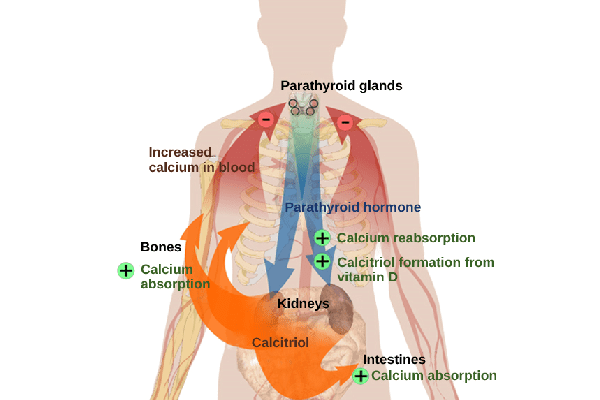
Diagnosis of hypercalcemia is carried out on the basis of a biochemical blood test, which determines the concentration of trace elements phosphorus, magnesium, as well as urea, creatinine in the blood.
At the same time, the parameters of bone metabolism are determined and the level of the content of parathyroid hormone and similar peptides in the blood is investigated.
Examine urine for the content of Bens-Jones protein in it.
The degree of urinary calcium excretion is assessed.
Diagnostic studies of the causes of hypercalcemia include:
- X-ray examination of various parts of the skeleton to detect resorption,
- Ultrasound of the kidneys to detect nephrolithiasis or changes in the renal parenchyma,
- Osteodensitometry for the diagnosis of osteoporosis.
Treatment of hypercalcemia is carried out depending on the severity and severity of the process.
Severe calcemia (or Hypercalcemic crisis ) requires immediate action:
- withdrawal of drugs that contribute to its development and maintenance;
- rehydration and restoration of diuresis;
- in the absence of pathology of the cardiovascular system and kidneys, 0.9% sodium chloride solution is administered;
- in the absence of the expected adequate diuresis, hemodialysis with a calcium-free solution is urgently indicated;
- control in parallel the content of magnesium and potassium in the blood;
- anti-resorptive drugs are introduced - biophosphonates;
- pamidronic acid is used (once, drip) in the case of paraneoplastic hypercalcemia;
- calcitonin is used as an alternative.
Treatment for moderate hypercalcemia involves:
- Exclusion from consumption of calcium-containing foods and medicines containing calcium,
- Loop diuretics and isotonic saline solutions,
- The use of drugs that reduce bone resorption (according to indications bisphosphonates, calcitonin, gallium nitrate, glucocorticoids).
Increased calcium has a toxic effect on the processes of tubular reabsorption in the kidneys, the glomerular filtration rate decreases. Hypercalcemia causes damage to the nervous system (impaired consciousness, lethargy, disorientation, depression, hallucinations). With hypercalcemia, the myocardium suffers, which changes one of the important characteristics - contractility. Hypercalcemia increases the toxicity of cardiac glycosides and increases blood pressure. Severe hypercalcemia can cause cardiac arrest.
The consequences of the hypercalcemia syndrome are reflected in the state of various organs and cause calcification of blood vessels, skin, stomach, lungs, heart; nephrocalcinosis.

Read

Read


























