Surgery diseases >>>> Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis.
Infected wounds (abrasions, punctures), as well as various purulent - inflammatory processes furuncle, abscess, phlegmon, panaritium, carbuncle, trophic ulcers) can be complicated by the development of lymphangitis, affecting lymphatic vessels of different sections located near the focus of purulent inflammation. The most common cases of lymphangitis are observed in the extremities with abrasions, abrasions, as well as in the area of the penis with trauma.
Lymphangitis is an acute inflammation of the vessels of the lymphatic system, and its occurrence is associated with the movement of pathogenic microflora from the primary focus to the interstitial space and capillaries of the lymphatic system. Through the lymph flow system, pathogens are carried through the lymph vessels of larger calibers and enter the area of the lymph nodes, which can lead to lymphadenitis. The danger of such a movement of the infection is that the inflammation of the vascular wall that occurs during this provokes the formation of exudate, fibrinogenesis and becomes the cause of thrombus formation, which prevents lymph flow. In severe cases, purulent lymphangitis can develop, which, spreading to adjacent tissues, involves the inflammatory process and blood vessels, as well as muscle tissue and other structures of the body that are in the path of the spread of the purulent process.
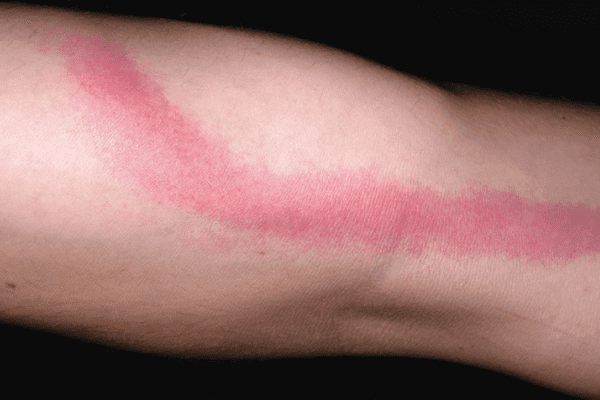
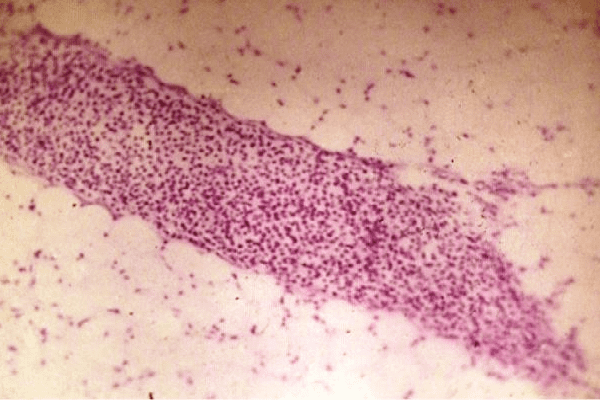
By the nature of the course, lymphangitis can be either acutely current or take on a chronic course. The depth of inflammation in lymphangitis depends on the depth of the location of the lymphatic vessels involved in the process, for this reason, lymphangitis may be superficial or deep. With superficial lymphangitis, capillary lymphatic vessels (reticular lymphangitis, reticular lymphangitis) are usually involved in the inflammatory process; with deep lymphangitis, large vessels are affected (trancular lymphangitis).
Signs of lymphangitis depend on the depth of the location of the affected lymphatic vessels:
- With superficial lymphangitis, a hyperemic area appears around the primary focus of infection and a mesh pattern (marble) is distinguished against the background of redness of the skin;
- Trancular (deep) lymphangitis is characterized by the appearance of redness on the skin in the form of a strip stretching along the direction of the lymphatic vessel towards the regional lymph nodes;
- The skin at the site of hyperemia is edematous (swelling is observed), on palpation, compaction and pain are felt;
- The general state of health worsens, the temperature rises;
- Symptoms of body intoxication (nausea, headache, etc.) are observed.
Lymphangitis requires timely and correct diagnosis (differentiated with erysipelas, superficial or deep phlebitis, phlegmon of soft tissues). To assess the depth of the inflammatory process in lymphangitis allows computer thermography.
Treatment of lymphangitis begins with the elimination of the primary focus of infection, which supports inflammation in the lymphatic vessels. Surgical treatment of purulent foci, treatment of infected wounds is carried out against the background of antibacterial therapy, taking anti-inflammatory drugs and detoxification measures. Chronically flowing lymphangitis provides for the imposition of ointment dressings on the inflamed areas, X-ray or laser irradiation.
Do not treat lymphangitis with folk remedies (especially warm up or massage the inflamed areas). Incorrect and untimely treatment of lymphangitis can lead to sepsis, since the lymphatic system very quickly transports the infection to various areas of the body. In addition, lymphangitis can cause irreversible changes in the lymphatic bed, which will lead to a disease such as elephantiasis.

Read

Read



























