Surgery diseases >>>> Signs of lymphadenitis
Signs of lymphadenitis.
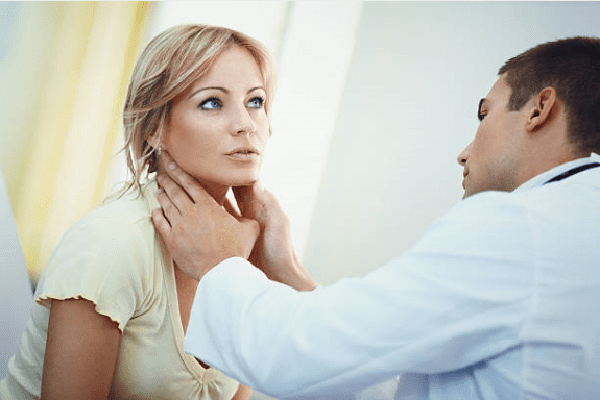
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the lymph nodes. Due to its specific function and the presence of a certain kind of immune cells, the lymphatic system itself is the body's defense mechanism against infection, and the lymph nodes, its peripheral centers, react to the presence of infection in the body. Their increase in size is a sign of an inflammatory process in a particular organ or tissues.
But sometimes, moving through the bloodstream, infectious agents penetrate from the bloodstream into the lymphatic bed, since the lymphatic system is closely connected with the circulatory system, as a supplier of lymphocytes. Getting to the nearest "strong point" of the lymphatic system - the lymph node, pathogens cause its infection.
Signs of lymphadenitis depend on the nature of the process. So with acute lymphadenitis, along with the general sign of an enlarged lymph node, painful symptoms appear, which often leads to difficult movements in the limb, around which the inflammatory process develops. The lymph node becomes dense to the touch. These symptoms are accompanied by fever, obsessive headaches. Chronic lymphadenitis proceeds with smoothed symptoms: low-grade fever, slightly swollen lymph nodes, subtle changes in general well-being.
Lymphadenitis can proceed as a serous or purulent inflammation, the distinctive features of a purulent from a serous process are: skin hyperemia in the area of a swollen lymph node (bright red), the lymph nodes merge with each other, forming a tight motionless formation, which is painful enough to the touch. The diagnosis of lymphadenitis is carried out on the basis of palpation of the lymph nodes and an assessment of their size and density, as well as on the basis of a study of the tissue of the lymph node obtained by puncture.
Differential diagnosis of lymphadenitis is carried out with lymphangitis, hidradenitis.
When treating lymphadenitis, it is taken into account that the disease can develop not only on its own (if the lymph node is injured), but also be a sign of other serious and dangerous diseases: tumors, tuberculosis, tularemia, plague, or a complication of vaccination (for example, with BCG).
The basis for the treatment of lymphadenitis with its specified infectious origin is antibacterial therapy. For specific pathogens, antibiotics are prescribed according to the identified strain and its sensitivity. With a nonspecific infection, a course of treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins) is carried out. The purulent form of lymphadenitis requires surgical intervention and drainage of the focus of suppuration. The wound is treated with proteolytic enzymes and antiseptics. If tumors that have caused lymphadenitis are found, radiation and / or chemotherapy is performed.
Lymphadenitis is a disease that can lead to severe complications in the form of osteomyelitis, abscess, sepsis and other diseases, because lymph nodes are participants in the immune system, and dysfunction of the lymphatic system is a blow to immunity. Therefore, lymphadenitis requires timely and adequate treatment.

Read

Read



























