Surgery diseases >>>> What is hydradenitis?
What is hydradenitis?
Acute purulent - inflammatory process that develops in the apocrine sweat glands is called "hidradenitis". The people used to call this disease "udder of female dog" due to the fact that the resulting multiple abscesses, located nearby, resembled a dog's nipples.
Apocrine sweat glands are located in the armpits, areoles, genitals, around the anus. They are larger in size than the eccrine sweat glands, which are ubiquitous. The secret of the apocrine glands contains cholesterol, as a result of which it acquires a whitish color. Very often, bacteria colonizing the surface of the skin enter the sweat glands through the excretory ducts and provoke an inflammatory process. But, sometimes the infection can be inside the apocrine glands, moving by the lymphogenous pathway. Among the bacteria that excite purulent inflammation of the apocrine glands, the most common are staphylococci, Escherichia, Proteus, and Pseudomonas. Purulent inflammation is especially difficult if the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus.
Since the apocrine glands significantly reduce their activity in old age, hydradenitis does not occur among the elderly. Hydradenitis can develop in both sexes, but in women it is more often located in the armpits, and in men - in the groin.
The causes of hidradenitis are associated with a number of factors:
- Decreased body immune responses;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Damage to the skin in the area of the location of the apocrine sweat glands, especially of a chronic nature: cuts at the time of shaving, abrasions, depilation;
- Damage to the sweat gland itself or disruption of its functions;
- Hyperhidrosis, which creates a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria;
- Violation of the rules of body hygiene;
- Generalized chronic infection;
- History of abscessed acne by the patient or his parents.
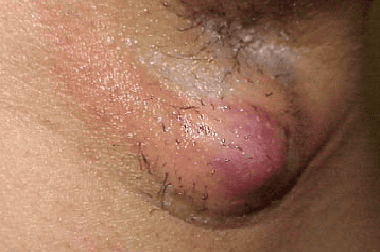
Signs of hidradenitis at the beginning of the development of a purulent process are similar to other purulent-inflammatory diseases: furunculosis, abscess, carbuncle. Very often, hydradenitis is confused with lymphadenitis. First, there is swelling of the skin, accompanied by itching and / or burning, followed by pain. As the tissue edema grows, the pain symptom also increases. Gradually, an abscess forms in the center of the swelling, which opens up with the release of purulent exudate. The cycle of development and maturation of the abscess takes up to two weeks. In the place of the opened abscess, a rough scar gradually forms. This is how hydradenitis proceeds in a mild form. But most often the adjacent apocrine sweat glands are involved in the inflammatory process, and multiple abscesses occur. The area of purulent inflammation occupies an increasing area, fistulas may form. As more and more sweat glands are involved, the healing time increases. Very often the process becomes chronic (relapses occur).
Improper or delayed treatment of hydradenitis can lead to phlegmon or sepsis.
Treatment of hidradenitis is based on drug therapy and surgery. When using drugs, the stage of development of the inflammatory process matters. At the stage of nodule or abscess formation, triamcinolone is injected into the focus of the incipient inflammation. At the same time, antibiotics of the macrolide or tetracyclines group and Isotretinoin are prescribed.
At a later stage, abscesses are opened, drained, antiseptics and proteolytic enzymes are used for washing, and antibiotics of the above groups are taken in parallel.
The entire scope of treatment is supported by immunostimulating therapy.
In complex cases of chronically current hydradenitis with multiple scars formed, excision of skin areas with subsequent transplantation of a skin flap is indicated.
Often, hydradenitis is difficult to treat, which may be associated with bacterial resistance to the drugs used, then it makes sense to conduct a biological study of the microflora of the areas affected by hydradenitis to establish its sensitivity to a number of antibiotics.
For the prevention of recurrence of hydradenitis, ultraviolet irradiation (artificial or under the rays of the sun), immunostimulating therapy are performed. Skin care of problem areas is of great importance. It is necessary to give up shaving, depilation of these areas of the skin (remove hair by carefully cutting), regularly wipe the skin in places where hydradenitis develops with weak antiseptic solutions and / or alcohol solutions of boric, salicylic acid, camphor alcohol. It is not recommended to take baths, they should be replaced with a shower. Clothes must be chosen from natural fabrics and loose cut so that it does not rub problem areas.
It is necessary to reconsider the diet and avoid the use of fatty, spicy foods, alcohol.

Read

Read



























