Medicine questions >>>> Enteropathy - what is it?
Enteropathy - what is it?
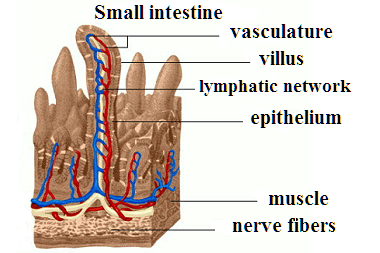
The term "enteropathy" is understood as pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the small intestine, which have various origins (infectious, allergic, toxic, radiation and others). Enteropathy can be the result of abnormal development of the vascular system, which is responsible for trophism of the tissues of the small intestine, abnormalities of connective tissue, disorders of the immune or endocrine system. Often, the exact cause of enteropathy cannot be established, which creates certain difficulties in its treatment (for example, in the case of autoimmune enteropathies).
Enteropathies are dangerous because, in the absence of adequate therapy, atrophy of the villi of the mucous layer, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the small intestine, crypt hyperplasia develop, which in turn becomes an obstacle to the normal absorption of nutrients by the body during digestion (the absorption of vitamin B 12, iron, folic acid, the level of magnesium ions (hypomagnesemia), potassium ions (hypokalemia) decreases , the absorption of proteins and fats (good cholesterol) is impaired . Enteropathy is characterized by inflammation of the mucous layer of the small intestine, accompanied by a specific clinical picture.
Typical signs of enteropathy:
- Bowel disorder (diarrhea),
- Increased gas production,
- Pain in the intestines,
- Possible bleeding (blood in the stool),
- Weight loss,
- Violation of the general state of health.
In the treatment of enteropathies, they adhere to etiotropic, symptomatic and pathogenetic therapy.
Etiotropic therapy involves adherence to a diet (for example, gluten-free), exclusion of allergenic products from the diet, to eliminate hypoproteinemia in case of impaired protein absorption, protein-containing solutions are administered intravenously (gamaglobulin, albumin). Prescribe iron, potassium, magnesium and vitamins. With an infectious origin of enteropathies, antimicrobial drugs are used (intestinal antiseptics, rifaximin - alpha).
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the use of glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressants, chemotherapy. To improve the function of absorption, enteroprotectors are used. Probiotics are prescribed to restore microbiocenosis.
Symptomatic therapy involves the use of enzyme preparations, intestinal motility regulators, according to indications.

Read

Read



























