Urology >>>> Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence.

The mechanism of urination is under the control of the central nervous system: the cerebral cortex, trunk and sacral spinal cord. As the bladder reservoir fills, the detrusor muscle relaxes, allowing urine to enter the bladder. In this case, the sphincters (internal and external), located on the neck of the bladder, are in a contracted state, preventing urine from flowing out. When the bladder is full, the smooth muscles of the bladder contract and the sphincters begin to relax one by one, allowing urine to drain. When a signal arrives from the cerebral cortex to the centers in the spinal cord that control urination, the external and internal sphincters and muscles of the urethra contract, which causes urination to stop.
If in any part of this process a failure occurs, involuntary urination occurs , uncontrollable by a person and called urinary incontinence.
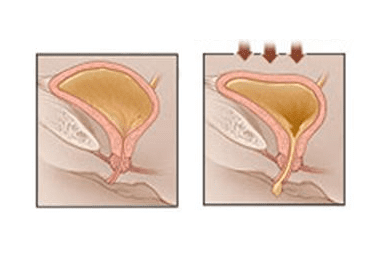
The causes of urinary incontinence are varied:
- Involuntary contractions of the detrusor muscle can cause imperative urination (imperative), urgent urination (uncontrollable), frequent urination, which are considered detrusor overactive or unstable and are not associated with neurological pathologies.
- Involuntary contractions of the detrusor (hyperreflexia) that are directly dependent on neurological disorders: in diseases of multiple sclerosis, parkinsonism, spinal cord injuries, stroke.
- Violation of the functionality of the pelvic floor muscles: hypermobility of the urethra, insufficiency of the urethral sphincters, weakness of the pelvic floor muscles.
- Abnormal location of the mouth of the urethra.
- Pelvic organ prolapse: bladder, uterus, rectum, vagina
There are several risk factors for the development of involuntary urination:
- The age of a person (women over 40 and men over 60),
- Gender (features of the anatomical structure of the obturator system of urination),
- Infectious - inflammatory processes in the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis ),
- Tumors
- Hormonal disorders
- Excessive physical activity (especially heavy lifting),
- Pelvic nerve damage,
- Overestimated body weight,
- Surgical interventions in the pelvic area,
- Pregnancy (in case of weakening of the pelvic floor muscles) or difficult labor,
- The state of the structure of the connective tissue in the pelvic region (collagen content decreases),
- Genetic, anatomical, or neurological abnormalities.
Urinary incontinence can occur not only due to anatomical or functional disorders, but also as a result of stress factors: fright, laughter, physical exertion, coughing. The process of urination can be provoked by sounds (murmur of water, creaking, rustling) or a sharp drop in temperature when moving from a warm atmosphere to a cold one. Being drunk can trigger urinary incontinence.
Treatment of urinary incontinence includes several methods, each of which is applied depending on the problems identified during the diagnosis.
Medical treatment of involuntary urination is used, as a rule, for all variants of the disease. Prescribe drugs that inhibit the activity of the contractile muscles of the bladder. In inflammatory and infectious processes, antimicrobial therapy is performed.
Surgical treatment of urinary incontinence is performed in cases of urinary incontinence due to an overflow of the bladder or in cases of stress factors of urinary incontinence. Surgical treatment is not indicated for urinary incontinence associated with neurogenic disorders, with prolapse of the pelvic organs. Surgical treatment is suitable for women due to the appropriate anatomical features of the female body. A loop is made of inert material, which is fed to the neck of the bladder or urethra, and its ends are removed through small holes in the pubic region. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and laparoscopic method.
Urinary incontinence in men is treated with antispasmodics, alpha-blockers (with benign prostatic hyperplasia), as well as drugs that inhibit the production of dihydrotestosterone (causes of prostatic hyperplasia), drugs that relax muscles and block nerve impulses (tricyclic antidepressants).
It is possible to inject collagen, special gels into the bladder neck area, and botox.
Physiotherapy treatment: ozone therapy, electrical stimulation.
A set of exercises for men and women, allowing you to train the pelvic muscles and training the rhythm of urination in time.
When carrying out any measures to restore normal urination, it is not recommended to take synthetic or herbal diuretics and foods that cause a diuretic effect (watermelons, melons, cucumbers, parsley, cranberries).

Read

Read



























