Otolaryngology >>>> Why is cholesteatoma dangerous?
Why is cholesteatoma dangerous?

Cholesteatoma is a tumor-like growth of an encapsulated mixture of dead epithelial cells, accumulations of cholesterol and other substances, surrounded by connective tissue. Outwardly it looks like a tumor, but it is not. As a rule, it forms in the middle ear and tends to grow into anatomical structures adjacent to the middle ear (including the mastoid process, paranasal sinuses).
The proliferation of cholesteatoma causes irreversible destruction of the structure of bone tissue, causes destruction of the auditory ossicles and temporal bone and other anatomical structures. The process of destruction of bone tissue in cholesteatoma is caused by two reasons:
- the process of bone resorption against the background of mechanical pressure arising from the growth of the cholesteatoma ;
- carious destruction against the background of a corrosive purulent process.
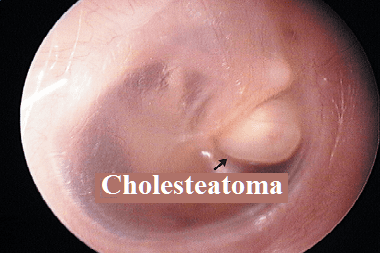
Cholesteatoma is dangerous because destroying bone structures on its way, creates an entrance gate for infection to enter the skull, provokes inflammatory processes (purulent labyrinthitis, periosinus or extradural abscess) and can lead to brain abscess, cerebral edema, inflammation of the meninges, hearing loss, paresis or neuralgia of the facial nerve.
The causes of cholesteatoma are not fully understood, but there is a scientific version that the impetus for its development is given by abnormal germination of epidermal tissue through the damaged tympanic membrane against the background of chronic otitis media or tubo-otitis.
Diagnosis of the presence of cholesteatoma is carried out using otoscopic and tomographic tissue examination. More reliable information can be obtained with surgery.
Typical signs of cholesteatoma:
- Pain and other sensations similar to symptoms of purulent otitis media,
- Cheesy, whitish discharge from the ear,
- Thick discharge from the nose (with damage to the maxillary sinuses),
- Hearing loss,
- Disturbances in the work of the vestibular apparatus,
- Dizziness,
- Headaches.
Treatment of cholesteatoma with conservative methods is not successful, therefore it requires surgical intervention in order to remove the formation. In parallel with the operation, plastic surgery of the tympanic membrane, reconstruction of the auditory ossicles and other damage to the bone tissue are performed. After removal of the cholesteatoma, the adjacent tissues are treated (washed) with antiseptic solutions and enzymes to remove the remnants of pus and destroyed tissue particles.
The prognosis for the treatment of cholesteatoma with timely surgical intervention is favorable, but due to the fact that the signs of cholesteatoma do not appear immediately, but as it grows, then, even with the slightest suspicion of trouble in the middle ear, it is necessary to consult a doctor for diagnostics.

Read

Read



























