Urology >>>> Causes of urolithiasis
Causes of urolithiasis.
To date, there is no unequivocal opinion about the causes of the formation of stones in the urinary system (the so-called urolithiasis). But there are many factors contributing to the development of this phenomenon, identified in the process of researching this issue by scientists.
- Disruptions in the body's metabolic processes, manifested in such disorders as: an increased level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) or in the urine (hyperuricuria), an increased level of calcium salts in the urine (hypercalciuria), an increased level of phosphate salts in the urine (hyperphosphaturia), an increased level oxolate salts in the urine (hyperoxaluria) promote the formation of insoluble salts that form in sand (microliths) or small stones (calculi) and are located in the organs of the urinary system.
- Some diseases contribute to the formation of a precipitate in the form of crystals of soluble salts (crystalluria).
- A change in the acidity level of urine affects its mineralization: with increased acidity, urates, oxolates, uric acid are formed. When urine is alkalized, ammonium urate salts or phosphates tend to form.
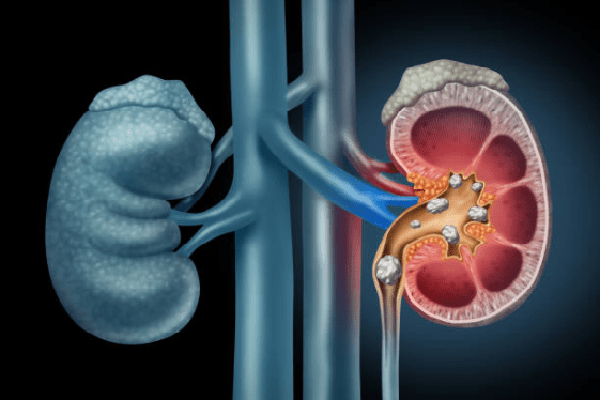
These metabolic disorders occur for a number of reasons, the most significant of which are:
- Enzymatic disorders
- Hereditary or acquired endocrine disorders
- Hypovitaminosis
- Disorders in the digestive system (including gastrointestinal diseases)
- Chronic diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis)
- The chemical composition of drinking water and food
- Fluid intake regimen (not enough)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Kidney injury
- Abnormal organ development
- Narrowing of the lumen of the urinary tract (congenital or acquired)
What are the stones with urolithiasis.
Stones formed in the urinary system are subdivided into types depending on the salt composition:
- Cystine - the amino acid cystine, poorly soluble in water, soft, soluble by drugs
- Struvite - ammonium orthophosphate and calcium carbonate, rapidly growing, coral-like, fragile, poorly soluble, but friable
- Xanthine - crystallization of xanthine due to a deficiency of the enzyme xanthine oxidase, do not respond to conservative treatment, poorly soluble
- Urate - salts of uric acid, loose, easily soluble
- Phosphate - calcium salts of phosphoric acid, difficult to treat
- Oxolate - salts of oxalic acid, do not dissolve
- In smaller quantities, there are: silicate, triamterene, carbonate stones, the composition of the substance responsible for their formation corresponds to the name of these stones.
Stones have the ability to form in different parts of the urinary system, and depending on where the stone is formed, urolithiasis acquires a specific name:
- with the formation of kidney stones - nephrolithiasis;
- with the formation of stones in the bladder - cystolithiasis;
- with the formation of stones in the urethra (ureter) - ureterolithiasis.

Read

Read



























