Traumatology >>>> Ankle fracture - signs and treatment
Ankle fracture - signs and treatment.

The ankle joint is one of the most difficult joints, the injuries of which are always difficult to recover. This is due to the special structure of the joint, which allows you to move the foot up and down, right and left. It is this set of movements in the ankle joint that causes ankle fractures. The ankle is one of the sides of the ankle joint (the so-called ankle fork) - two processes of the tibia of the lower leg (part of the leg from the ankle to the knee). The ankle is divided into lateral (outer protruding bone) and medial (inner protruding bone).
An unsuccessful twist of the leg during movement, an emergency stuck of the foot in a vice of various designs (for example, in an accident), an unsuccessful fall with a turn of the foot, a fall of a heavy object on the ankle area is the reason for a fracture in the ankle area.
Ankle fractures are single-malleolar (one process of the tibia is broken off), two-malleolar (both lateral and medial processes are broken off) and trilocular (both processes are broken off and the anterior or posterior part of the tibia itself).
Depending on the complications with which the fracture occurs (open, splinter with displacement of fragments, closed, without displacement of fragments), the complexity of the restoration of the leg and the work of the ankle joint will depend.
Signs of ankle fracture:
- pain in the ankle joint, but not in the soft tissue area, but in the tibia;
- swelling of the ankle;
- suspension of the foot (change in the angle of inclination between the foot and lower leg);
- severe bruising, extending not only to the ankle, but also to the sole and arch of the foot;
- the inability to lean on the foot painlessly.
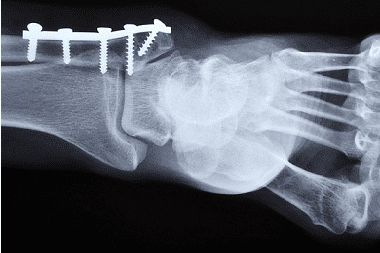
Ankle fractures can be complicated by dislocations, ruptures of the ankle ligaments and sprains of the ligaments of the joint, for this reason, treatment of ankle fractures begins with repositioning the dislocations, if this is observed, and matching the fragments. The actions of the traumatologist are supported by X-rays and computed tomography. Joint reduction and repositioning are performed under local anesthesia. If, during a fracture, parts of the bones and anatomical structures of the joint disperse, osteosynthesis is performed using various metal fasteners. Next, the ankle is immobilized for four weeks with a single-ankle fracture, for eight weeks for a two-ankle fracture, and for 12 weeks for a three-ankle fracture.
If it is impossible to connect correctly displaced bones and joint structures, surgical intervention is required, while drainages are placed before immobilization (plaster cast) and the wound is washed with antibiotics. An open fracture of the ankle, complicated or uncomplicated by other injuries, also requires surgical treatment.
It happens that a fracture in the ankle area is insignificant, and the patient does not go to a medical facility, then such a fracture is classified as an old one, and if a pain symptom develops in the future, an operation is performed to restore the connection of the bones.
The prognosis for ankle fracture depends on the severity and severity of other types of ankle injuries. With a successful reduction, all structures are restored, and after a while, it is only necessary to methodically develop the joint. In case of untimely treatment, complicated fine fractures in the ankle area, recovery procedures require bone grafting and a long rehabilitation period.

Read

Read



























