Traumatology >>>> Intra-articular fracture - signs and treatment options
Intra-articular fracture - signs and treatment options.
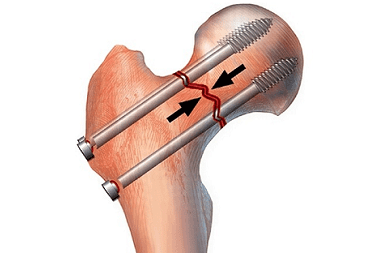
An intra-articular fracture is a complex injury in which the fracture site is located inside the joint cavity (inside the joint capsule). The most common cases are intra-articular fractures in the limb region.
The causes of intra-articular fractures lie in unsuccessful falls with support on the joint, twisting of the limbs with an excess of the possible range of motion in the joint, a shock of great force (when falling from a height, road accidents, sports, domestic and industrial mechanical injuries).
Signs of an intra-articular fracture:
- Sharp pain of high intensity,
- Impaired movement in the injured joint,
- Joint deformity,
- Bulging of displaced debris,
- Swelling of the soft tissue surrounding the joint,
- Bruising in the tissues around the joint,
- Ruptures of soft tissues in the joint area.
With an intra-articular fracture, not only the integrity of the bone can be violated, but also the cartilage can be damaged, and ligaments can rupture. While maintaining the integrity of the articular capsule, the fractured parts are retained inside the articular capsule and often reduce the mobility of the fractured joint elements. In addition to intracapsular fractures, rupture of the articular bag itself and the outflow of synovial fluid outward are possible.
Diagnosis of an intra-articular fracture is carried out by X-ray (in various projections), using MRI and arthroscopy.
Difficulty of joint restoration in case of intra-articular fracture is associated, as a rule, with the displacement of the fragments and the difficulties of their correct comparison, which violates the congruence of the parts of the joint (their exact correspondence in shape and surfaces to each other). Incorrect matching and restoration of the shape of the intra-articular elements leads to limitation of joint mobility to varying degrees or to its complete immobility. Even with a successful juxtaposition and fusion of bone fragments and / or parts of cartilage, rough surfaces can form, which, during the period of movement in the joint, will create traumatic friction, which will eventually lead to the development of arthrosis. The more fragments are formed during an intra-articular fracture, the more difficult it is to reposition the fragments, restore joint function and avoid future diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Complications of an intra-articular fracture can be contractures that complicate the rehabilitation of the joint after injury.
Treatment of an intra-articular fracture is correlated with the extent of the injury and the specific joint. The displaced broken off fragments are compared using distraction devices, skeletal traction. Intra-articular fracture without displacement is fixed with a plaster cast. The rehabilitation period, when the bandage is removed and the joint begins to develop, preventing the development of contractures, is of great importance in restoring joint mobility after a fracture. If it is impossible to restore the articulation of the joint (in the case of incomparable comminuted fractures), arthroplasty is performed.

Read

Read



























