Gynecology and Mammology >>>> What is bartholinitis?
What is bartholinitis?

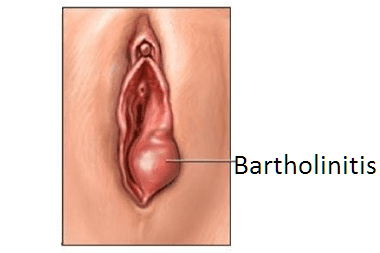
The inflammatory process that develops in one of the Bartholin glands (large Bartholin gland) is called bartholinitis. The Bartholin glands are located in the vestibule of the vagina. They secrete the vagina to keep it moisturized and lubricated. With bartholinitis, inflammation covers either the entire gland or only the excretory duct, blocking the secretion outlet. Outwardly, bartholinitis looks like a spherical growth protruding from the lumen of the vagina towards the labia.
The causative agents of bartholinitis are conditionally pathogenic (Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus, Candida fungus) or pathogenic microorganisms (chlamydia, gonococcus, Trichomonas).
The causes of bartholinitis lie in the creation of certain favorable conditions for the penetration of infection into the bartholin glands:
- Acute or chronic infectious processes in diseases of urethritis, vaginosis, colpitis;
- Penetration of infectious agents through the blood or lymph from infectious foci in diseases of pyelonephritis, cystitis, chronic tonsillitis and others;
- Violation of the rules of genital hygiene;
- Injuries to the excretory ducts of the glands during plugging or sexual intercourse;
- Failure to observe personal hygiene by a partner;
- Promiscuous sex;
- A weakened immune system response;
- Local hypothermia;
- Tight underwear or trousers causing glandular congestion;
- Postoperative complications of the genitourinary system.
Bartholinitis signs.
Bartholinitis can take the form of canaliculitis (inflammation of the excretory duct of the gland), cysts, or abscesses. Often canaliculitis precedes the development of the inflammatory process directly in the gland itself.
Initially, skin hyperemia appears in the area of the outlet duct of the Bartholin gland. Gradually, due to edema, the duct of the gland closes, which leads to the spread of inflammation throughout the gland. The secret, having no way out, begins to accumulate, the tissues swell, the inflammation turns into a purulent stage and a false abscess of the Bartholin gland develops. At the same time, pain symptoms appear in the area of the labia majora, which intensify during walking, during intercourse. There is a swelling in the area of one of the labia, which over time increases in size, sometimes closing the passage to the vagina.
The appearance of an abscess on the surface of the swelling suggests that the false abscess has turned into a true abscess of the Bartholin gland. In this case, the general condition may worsen: the temperature rises (up to 39 - 40 degrees). The pain in the area of swelling becomes twitching, sometimes the inguinal lymph nodes increase.
Sometimes the abscess opens on its own, but in some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary .
In the case of the formation of a cyst of the Bartholin gland, bartholinitis may be asymptomatic for many years or have a certain set of symptoms:
- Discomfort while walking, sitting, intercourse,
- Periodic pain in the labia majora area,
- A thickening is felt in the labia majora,
- Hyperemia of the skin over the swelling,
- The size of the swelling varies depending on the size of the cyst,
- The cyst may open on its own or continue to grow in size,
- The body temperature may rise to 38 in Celsius degrees.
Bartholinitis can be acute or chronic with periods of remission and improved well-being.

Read

Read



























