Infectious diseases >>>> Parvovirus infection
Parvovirus infection.
Parvovirus infection is an infection with a variety of clinical manifestations. Of the large family of parvoviruses that cause disease, only the Parvovirus B19 strain is dangerous to humans .
Parvovirus infection is a year-round disease, but most often its manifestations are observed in winter and spring. According to statistical studies, cases of parvovirus infection occur in childhood, since the majority of the adult population has antibodies to Parvovirus B19 developed by the immune system . The period when the virus enters the bloodstream is called viremia, it lasts about 6 days and is considered the time when the patient is contagious. At this time, the virus spreads by airborne droplets and blood contact.
The sings of parvovirus infection are:
- a general disorder of well-being,
- fever,
- headaches,
- itchy skin,
- myalgias,
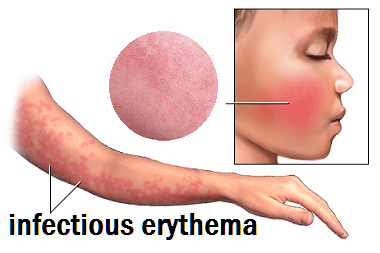
- spotty rashes on the cheeks, limbs and having a lace pattern (infectious erythema),
- signs of arthritis or arthralgia of the joints of the wrist, knee.
Due to the fact that some strains of parvoviruses have the ability to multiply only in the presence of adenovirus or herpes virus, which are used as helpers, they aggravate the course of parvovirus infection in sick people. In addition, in people suffering from immunodeficiency, hemolytic anemia or sickle cell anemia, parvovirus infection is accompanied by the destruction of erythrocyte precursor cells.
Parvovirus infection can cause an aplastic crisis in people with anemia or acute blood loss.- a condition characterized by the disappearance from the blood of reticulocytes - erythrocyte precursor cells (“young erythrocytes”, blanks for full-fledged erythrocytes). The characteristic signs of aplastic crisis are pallor, drowsiness, weakness, a drop in hemoglobin to a level that threatens life and requires blood transfusions. Parvovirus is also dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause dropsy of the fetus. Healthy people carry parvovirus infection without treatment.
Diagnosis of parvovirus infection is carried out using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of IgM and IgG immunoglobulins.
Treatment of parvovirus infection differs depending on the medical history of the patient and the severity of the infectious viral skin disease:
- Signs of aplastic crisis suggest inpatient treatment of the patient in a closed box, the same is required for chronic parvovirus infection;
- With aplastic crisis, blood transfusion is indicated;
- In patients with immunodeficiency and anemia, intravenous immunoglobulin is used;
- Infectious erythema does not mean treatment - it goes away on its own.
Parvovirus infection is dangerous by complications affecting the peripheral and central nervous system: meningitis, meningoencephalitis, encephalitis, peripheral neuropathy, chorea, paralysis.

Read

Read



























