Dermatology >>>> Miliums and atheromas are follicular cysts
Miliums and atheromas are follicular cysts.
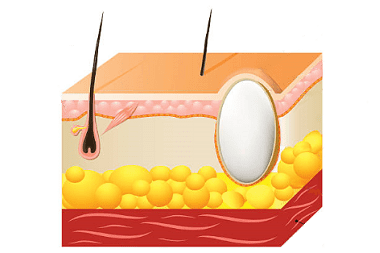
Milia, or whiteheads, are miniature epidermal cysts that develop at the mouth of the follicle and sebaceous gland. Milium can form as an independent formation in people with a predisposition to this, or accompanies diseases of a bullous nature (with a rash of subepidermal blisters), or occurs after an injury to the follicle, sebaceous gland as a result of abrasion, sunburn, or cosmetic procedures for cleansing the skin of the face (dermabrasion, peeling with scrubs).
Very often, the appearance of milia is associated with hormonal imbalances in the body, with disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, with hypovitaminosis, and a violation of facial skin hygiene. All these causes of milia lead to increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, metabolic disorders in the metabolism of fats. Therefore, in order to prevent the occurrence of whiteheads, it is necessary to refrain from excessive consumption of spicy, fatty, sweet foods, revise the procedures for cleaning the skin of the face and choose the least traumatic types of skin hygiene.
Externally, milia or whiteheads appear as solitary or scattered whitish-yellow nodules. In fact, a million is a follicle or sebaceous gland clogged with a fatty secretion. Milliums are superficial cysts located not deep in the dermis.
Miliums are located in the forehead, temples, cheeks, eyelids, in the area of hair follicles of the extremities or trunk. Miliums are painless acne, but sometimes inflammation can occur when their superficial membrane is injured.

When diagnosing milia, a differential diagnosis is made with trichodiscoma, xanthelasma, syringomas, fibrofolliculoma, fibroma.
Treatment of whiteheads is based on special procedures for opening and scraping (curettage) of the contents of the cyst, followed by antiseptic treatment. Self-extrusion of milia does not lead to the desired results, but, on the contrary, is a factor stimulating an increase in milia in size. Therefore, all procedures for the removal of milium are carried out in beauty salons and equipment designed for these purposes. Today, there are several hardware methods for removing milia: using electrocautery, laser or radio wave method. After the removal procedure, small wounds remain that heal without a trace within two weeks.
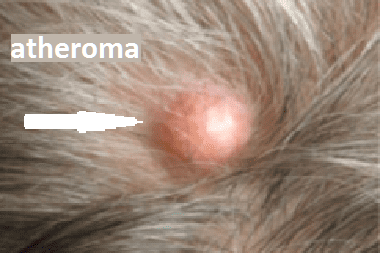
Atheroma (synonym: sebaceous cyst) is a hair cyst, clinically indistinguishable from an epidermal cyst, but having no connection with the epidermis, that is, separated from it by a dense wall, located deep enough in the thickness of the dermis. The inner content of the cyst is represented by keratin and cholesterol inclusions. Atheroma is prone to dehydration, when its wall breaks through, a purulent - inflammatory process can develop, causing painful symptoms. Unlike epidermal cysts, atheromas are located mainly in the scalp. At the site of the atheroma, there is no hair, and signs of atrophy are noticeable on the skin.
The causes of atheroma are associated with trauma to the hair follicle or sebaceous gland duct, which are clogged and prevent the secretion of the sebaceous gland from continuing to function. As the sebaceous secretion accumulates, the atheroma increases in size.
Treatment of atheroma is similar to the treatment of lipoma and consists in removing the atheroma together with the capsule, or in scraping the contents of the atheroma. A well-proven method of radio wave removal of atheroma, which is carried out under local anesthesia, does not have complications in the form of bleeding and prevents the re-development of atheroma.

Read

Read



























