Dermatology >>>> Folliculitis
Folliculitis.
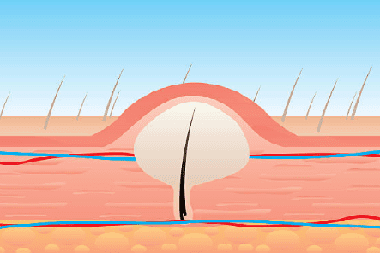
A purulent inflammatory process of the hair follicle is called "folliculitis". The inflammatory process can be located in the upper part of the hair follicle or spread to a deeper layer if the purulent process covers the entire follicle.
The mechanism of folliculitis is directly related to the penetration of an infectious agent into the injured follicle. The causative agent of folliculitis can be a bacterium (Staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Treponema pallidum), a fungus (Phyrosporum, Pityrosporum, Candida albicans, Trichophyton), a virus (herpes simplex infection), herpes simplex infection.
When an infection enters the follicle cavity, a papule forms in its mouth, and after a while an abscess forms in the center of the papule - a pustule, while the hair grows through the pustule. When the abscess resolves itself, erosion remains in its place and a crust forms. With a superficial inflammatory process, folliculitis passes without leaving traces; with a deep purulent lesion, there is a risk of developing a furuncle. Folliculitis develops and goes away within a few days, but in case of complications, the process can be delayed. The duration of the healing process can be influenced by a decreased response of the immune system, diabetes mellitus, harmful environmental conditions, skin diseases, and poor skin hygiene.
The causes of folliculitis that provoke infection in the hair follicle:
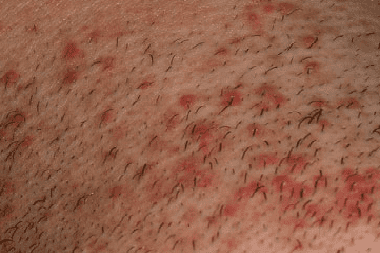
Folliculitis signs are manifested in the form of multiple rashes, itching, burning on the skin. Depending on what kind of infection was that provoked folliculitis, the rash externally differs:
- With a viral or parasitic infection, they resemble bubbles,
- With a fungal or bacterial infection, it may look like papules or nodules.
Folliculitis is usually located in places of hair growth: face, neck, scalp, armpits, back, chest, limbs, groin, perineum.
Differential diagnosis of folliculitis is carried out with diseases similar in symptoms: rosacea, acne, medicinal toxidermia, irritation with chemically active substances, vitamin deficiencies, lupus erythematosus, ingrown hair (pseudofolliculitis), Grover's disease, impetigo.
Folliculitis treatment depends on the identified infectious agent:
For bacterial folliculitis, fusidic acid or mupirocin is prescribed. If Staphylococcus aureus is detected, clindamycin is prescribed because the bacterium is resistant to methicillin. With deep purulent processes in the follicle, fluoroquinols, cephalosporins, macrolides are prescribed. Folliculitis caused by Pseudomonas ("hot bath" folliculitis) in mild cases resolves on its own within a week, in severe cases it requires taking ciprofloxacin. Systemic antibiotics are usually prescribed in cases of widespread and chronic disease. Often the cause of folliculitis caused by gram-negative bacteria is precisely the intake of antibiotics, in which case these antibiotics are canceled, and benzoyl peroxide is used.
Folliculitis caused by a fungal infection requires the appointment of antifungal drugs, topical application of shampoos containing selenium, azoles, zinc. For dermatophytic folliculitis, itraconazole, terbinafine, fluconazole are used.
Folliculitis caused by the Demodex folliculorum mite requires the use of metronidazole tablets and as part of Metrogyl gel, invermectin or 5% -permethrin cream.
Folliculitis of viral origin is treated with antiviral drugs for external use, ointment Acyclovir and / or inside (Acyclovir, Famvir, Valtrex).
There is a so-called eosinophilic folliculitis that occurs in HIV-infected patients. It is caused by a viral infection or autoimmune processes. With eosinophilic folliculitis, CD4 + cell populations are reduced. Treatment for this form of folliculitis is based on antiretroviral therapy.
Prevention of folliculitis consists in improved hygiene of the skin surface in problem areas, refusal to wear tight clothes, use of antiperspirants or talcum powder with increased perspiration, regular treatment of problem areas on the skin with benzoyl peroxide, use of antiseptic soap, refusal from shaving, depilation.

Read

Read



























