Musculoskeletal system >>>> What is joint hypermobility?
What is joint hypermobility?
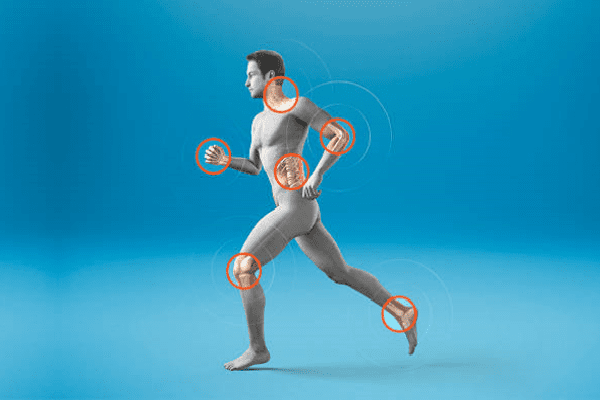
Hypermobile joints are joints that have excessive extensibility or overextension (hyperextension, from the English "hyperextension"). Due to the weak structure of the connective tissue of the joint capsule, poor in collagen, which is responsible for elasticity, the tissues of the articular apparatus become excessively stretchable, which allows movements in the joint that go beyond its anatomical capabilities, but give the joint excessive flexibility. Excessive movement in the joint is considered a pathology, since it overloads the ligamentous apparatus and often leads to its injuries.
People whose joints are prone to overextension may have different degrees of hypermobility, but the diagnosis of “joint hypermobility” can be made using the Beyton method. Its essence lies in the fact that a person is offered to perform five exercises:
- Extend the little finger of the hand to its perpendicular position in relation to the hand (or at an angle of more than 90 degrees);
- Press your thumb to the inside of your forearm;
- Bend your knees back (overextension at an angle of more than 10 degrees);
- Bend your elbows in the opposite direction (overextension at an angle of more than 10 degrees);
- Standing on your feet shifted together, tilt your torso and touch the floor with your palms without bending your legs.
If all these exercises are performed successfully, then you are the owner of joint hypermobility syndrome (but three out of five exercises performed are enough for the diagnosis).
Usually, excessive joint mobility (overextension) may not cause trouble for a person, but, on the contrary, give him advantages when doing some types of gymnastics. But it happens that at a certain period of time a person with hypermobile joints begins to experience a feeling of discomfort in the articular apparatus, and may also be subject to the development of certain diseases of the musculoskeletal system: spontaneous fractures, spontaneous sprain, pain in the joints or spine, subluxations, ruptures ligaments. Such joints do not tolerate physical activity (including weight lifting, high heels, excess body weight).
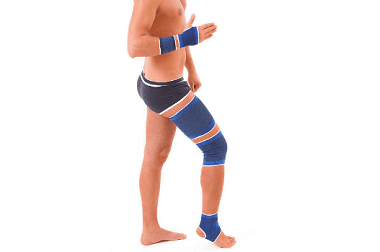
People who have noticed signs of hypermobility joints will not be hurt by wearing orthoses as limiting joint movement and to prevent future problems in the articular apparatus. With hypermobility of the joints, it is also worth avoiding classical yoga or other types of gymnastics aimed at stretching the ligamentous apparatus. Exercises must be selected individually and not involve the joints, but only strain the muscle tissue. Such exercises are called static or slow dynamic, and do not use weights when performing them.
Scientists consider the causes of joint hypermobility in the relationship between genetic predisposition (close relatives may have joint hypermobility) and disorders of connective tissue formation (a particular case of STD is connective tissue dysplasia or collagenopathy). For this reason, joint hypermobility syndrome is not considered an acquired disease. Joint hypermobility is observed already in childhood and is often a concern for parents. And not in vain, because this symptom may be just one of the manifestations of much more complex diseases associated with STD. Connective tissue dysplasia can also manifest itself in excessive stretching of the skin (the appearance of stretch marks) throughout life, increased skin trauma, the development of scoliosis or kyphosis, chronic sprain, a tendency to form hernias, prolapse of internal organs, muscle weakness.

Read

Read



























