Musculoskeletal system >>>> Ankylosis of the joint
Ankylosis of the joint.
Impaired movement in the joint, leading to its complete immobility due to pathological tissue modification is called "ankylosis of the joint". Ankylosis translated from Greek means "ossification".
Joint immobility develops as a result of pathological fusion of bone, cartilaginous and / or connective tissue of the articular joints with a change in the biophysical characteristics of these tissues. Fabrics lose elasticity, stretch ability, shock absorption. The cause that initiates fusion processes can be chronic inflammation in the joint caused by trauma, infection, tissue metabolism disorders, complications after a treated fracture, dislocation, stretching, degenerative processes due to a violation of the trophism of the joint tissues (impaired blood circulation in the joint area) or caused by age-related changes in the structure fabrics.
Ankylosis can also be caused by a sedentary lifestyle that does not properly load the tissues of the joint, and any sudden load, for example, in the form of lifting weights, can lead to microtrauma and inflammation.
Depending on what kind of tissue is being transformed and constraining the movements of the structural elements of the joint, there are bone ankylosis (true), cartilaginous ankylosis, fibrous ankylosis.
Signs of ankylosis of the joint:
- Painful sensations during movement in the joint, accompanied by a loss of range of motion of the joint,
- Limitation of mobility in the joint, followed by its complete loss,
- Changing the physiologically correct position of the limb.
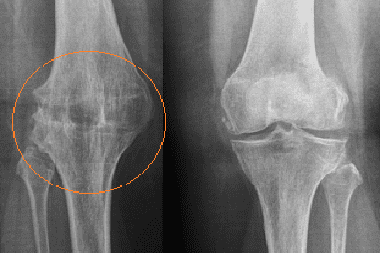
X-ray examination helps to clarify the type of ankylosis:
- with bone ankylosis, the joint space between the bones is absent, and one bone structure smoothly passes into another;
- with fibrous ankylosis, the joint space is narrowed, and the articular surfaces of the bone structures are flattened.
Treatment of ankylosis of the joint is carried out by surgical methods:
- Arthroplasty - forced expansion of the ends of the articular structures with simultaneous plastic surgery of the articular surfaces;
- Osteotomy - straightens the deformed articular bone structures;
- Alloplasty - replacement of damaged joint structures made of artificial materials or donor tissues;
- Homoplasty - transplantation of donor bone structures (including a whole joint);
- Endoprosthetics is a complete replacement of a joint with an artificially designed joint made of metal, ceramics, and extra strong plastics.

Read

Read



























