Infectious diseases >>>> Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis.
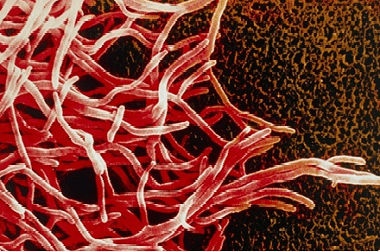
Actinomycosis (or radiant fungal disease) affects animals and humans. This fungal disease is quite common in many countries. The causative agents of actinomycosis are several species of radiant fungi of the genus Actinomyces. The fungus owes its name to the peculiar arrangement of the mycelium filaments in the form of rays. Fungi of the genus Actinomycetes as saprophytes live in the oral cavity, in the upper respiratory tract, in the digestive tract, and infect bone tissue.
Ways of infection with a fungal infection when detecting actinomycosis are often not traced, but fungi of this kind are found in water, soil, grass, which allows the infection to spread exogenously (contact - household, airborne dust, airborne droplets) along with endogenous (lymphogenous, hematogenous). Predisposing factors for infection with actinomycetes are reduced immune responses, weakening of the body during acute respiratory diseases, influenza and a number of other diseases that undermine the state of the immune system.
Actinomycosis – signs.
Depending on where the primary infection with actinomycosis occurs, the signs of its manifestation are also distinguished.
When the skin is damaged, dense bumps of a burgundy-cyanotic color with pustules appear in the thickness of the skin. The cutaneous form of actinomycosis is also characterized by the formation of atheromas, dense nodes or ulcers, which gradually turn into fistulas and are accompanied by tissue necrotization in this area.
Cervical and maxillofacial forms of actinomycosis are manifested in the form of granulomatous growths of tissues (intermuscular tissue, subcutaneous tissue) with the subsequent formation of fistulas, which leads to swelling and asymmetry of the face.
The osteoarticular form of actinomycosis proceeds according to the principle of osteomyelitis, with the infiltrate reaching the surface through fistulas. This form of actinomycosis is accompanied by painful symptoms in the area of the affected bones and joints.
The thoracic form of actinomycosis of the lungs proceeds with an increase in temperature to subfebrile and slightly higher, with a dry cough. Gradually, the nature of the cough changes, purulent sputum (possibly mixed with blood) begins to recede, a smell of dampness appears when breathing, pains develop when breathing and at the time of coughing. An infiltrate is formed in the lungs, which spreads from the center to the periphery and can spread not only to the bronchi, pleura, but also come out in the form of fistulas on the skin surface in the chest or lumbar region. As a complication of the thoracic form of actinomycosis, the mediastinum, heart, esophagus, and mammary glands are affected.
The abdominal form of actinomycosis affects the digestive tract throughout its entire length. It manifests itself in the form of intestinal obstruction, enterocolitis, acute appendicitis. The patient complains of pain in the abdomen, bladder, rectum. The infiltrate spreads towards the liver, kidneys, spleen or abdominal wall, comes out in the form of fistulas.
Mycetoma or actinomycosis of the foot is manifested by a compaction on the sole in the form of one or more nodes of a reddish-cyanotic color. The foot swells, hurts when walking. Over time, fistulas form on the surface of the foot.
There are cases of lesions by the fungus of the genus Actinomyces of the genitourinary system, the Central nervous system, individual organs (nose, tongue, middle ear, eyes, tonsils, salivary glands, thyroid gland).
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out on the basis of a microbiological study of purulent contents. With actinomycosis of the lungs, radiography shows the location of the foci of the infiltrate.
Actinomycosis - treatment.
In the treatment of actinomycosis, immunomodulators are used - the drug Actinolizat is injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly. To prevent the addition of a secondary infection, antibiotic therapy is used (benzylpenicillin, tetracycline antibiotics, macrolides).
Surgical intervention is carried out with the aim of excision of the affected tissues, drainage of purulent cavities. If significant areas of the lungs are affected, lobectomy is performed.

Read

Read



























