Infectious diseases >>>> Toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome.
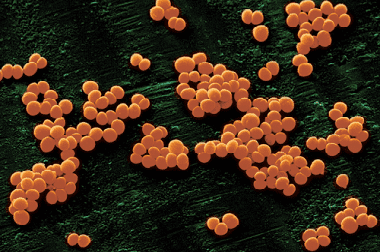
Toxic shock syndrome is a condition associated with the toxic effects of highly virulent bacteria and viruses on the body. The most common culprits in the development of toxic shock are Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), Streptococcus pyogenes (Streptococcus).
Typical signs of toxic shock syndrome:
- Sudden fever and chills are the first signs;
- High temperature (above 39 in Celsius);
- Hyperemic skin (looks like a sunburn or thermal burn);
- Rash on the skin, after healing - flaky (on the palms and feet);
- Inflamed mucous membranes (pharynx, conjunctiva, vagina);
- Sore throat;
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Myalgia in the limbs, back;
- Decrease in blood pressure;
- Headache.
The general condition of the patient changes to such an extent that he looks seriously ill.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with influenza, septic shock, scalded skin syndrome, staphylococcal scarlet fever, Kawasaki disease.
Treatment of toxic shock syndrome consists in intensive detoxification measures: restoration of water and electrolyte balance, the introduction of large amounts of fluid, increased blood pressure, respiratory control, the use of antibacterial agents effective against staphylococcus or streptococcus (cephalosporins of the second and subsequent generations, Vancomycin), in severe cases, the introduction of a specific immunoglobulin.
The most common causes of the manifestation of toxic shock syndrome are damage to the skin and mucous membranes, due to the fact that staphylococci and streptococci are conditionally pathogenic microflora, which is always present on the surfaces of the skin and mucous membranes, and infection with such microorganisms is easy to obtain with various kinds of injuries or even minor abrasions. The phenomenon of toxic shock syndrome is directly related to the failure of the body's immune responses to antigens, the inability to develop antibodies to the toxins of these microorganisms at the right time.

Read

Read



























