Cardiovascular system >>>> Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia.

The heart muscle (myocardium) of a person distills blood, acting on the principle of alternating contraction and relaxation of various parts of the heart. The rhythm, frequency and sequence of such contractions and relaxations are in a certain order, and the whole structure works automatically. Due to various circumstances, this order can be disrupted and the myocardium begins to malfunction in rhythm, changes the frequency, rhythm, sequence of contractions and relaxation. This is how a phenomenon called arrhythmia in medicine occurs.
The causes of arrhythmia are associated with functional disorders and / or organic lesions of the myocardium. The basis of arrhythmia is electrophysiological disturbances in the myocardium, or rather disturbances in the conduction of an electrical impulse that causes successive contractions of various parts of the heart. These disorders are diverse and determine the variety of types of arrhythmias and their complex combinations.
The work of the myocardium is tied to the functioning of the sinus node, which is the main generator of impulses and sets the rhythm of all cardiac activity. A state is considered normal when the heartbeats at rest while awake are 60-80 beats per minute (during sleep, the frequency of beats decreases, and during physical activity it increases). The sinus node generates electrical impulses, sending them to the ventricles and atria. In addition to the sinus node, there are several more nodes in the myocardium, which are assigned the functions of the main driver of the heart in case of violations in the sinus node.
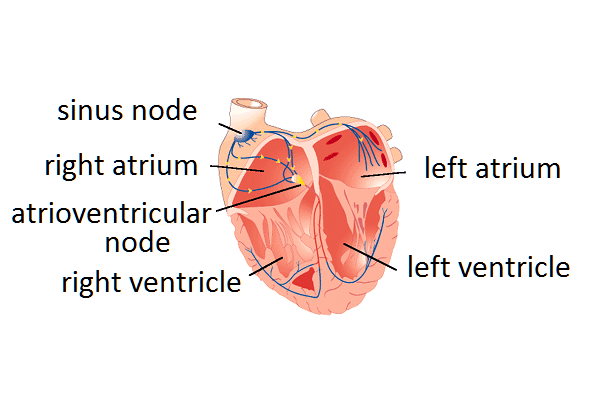
There are the following disorders in the work of the myocardium:
Violation of the automatism of contractions and relaxation
There is a decrease or increase in the automatism of the sinus node. A decrease in automatism leads to the development of a replacement rhythm (that is, other parts of the myocardium are included in the process) - the frequency is 20-40 beats per minute. An increase in automatism is a rare phenomenon, it has a frequency of up to 100 beats per minute, it causes parasystole or extrasystole.
Impulse conduction disorder (or blockade)
This slows down or interrupts the conduction of pulses in certain sections of the path. Such violations are called blockades and are divided into several types:
- Slow conduction of impulses (incomplete blockade)
- Some impulses are not delivered (incomplete blockade)
- Interruption of impulses (complete blockade) - dangerous by cardiac arrest
Hidden impulse conduction
Such impulses do not reach the target, but cause a local temporary blockade.
Pulse circulation/p>
In this case, the impulses pass to the target, but return along a parallel path (a section of the conducting system that duplicates the main path of the impulse), as a result of which a premature repeated contraction of the heart occurs. Such circulating impulses, which have stability, lead to extrasystoles and tachycardia.
All myocardial disorders are detected using an electrocardiogram (ECG) and thus differentiate the types of arrhythmias.
Arrhythmia signs:
- feeling that the heartbeat is felt, although in everyday life it is not noticeable
- feeling of tightness in the chest
- increased breathing rate
- dizziness
- weakness
- accelerated pulse at rest - more than 100 beats per minute (tachycardia, extrasystole, atrial fibrillation)
- slow heart rate at rest and wakefulness - less than 60 beats per minute (bradycardia)
- Irregular, skipping beats, pulse (irregular myocardial rhythm)
The prerequisites for the occurrence of arrhythmias can be:
- various deviations in the work of organs and their systems (heart failure, myocardial infarction, heart enlargement, congenital heart anomalies),
- metabolic disorders in the body (hyperthyroidism, increased adrenaline due to improper adrenal glands, decreased blood sugar),
- lack of useful elements (potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium),
- medicines that disturb the heart rhythm (antidepressants, beta-blockers, stimulants of nervous activity).
Arrhythmias are dangerous because they cause disturbances in the blood supply to organs, provoke the development of insufficiency of the coronary vessels or the heart, increase the likelihood of thromboembolism, and may cause cardiac arrest.

Read

Read



























