Dermatology >>>> Why does urticaria appear?
Why does urticaria appear.
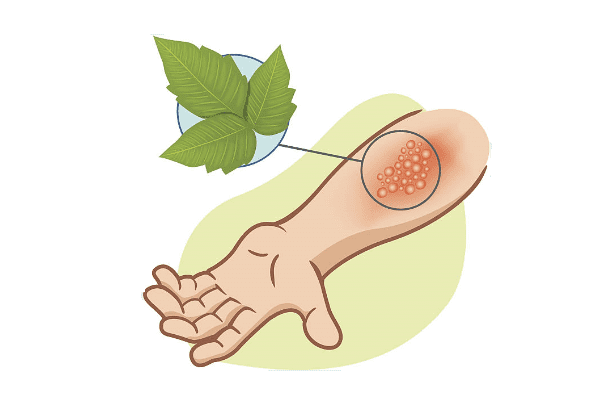
Urticaria is a disease belonging to the group of allergic dermatoses, which is accompanied by the sudden appearance on the skin (or mucous membranes) of itchy rashes in the form of blisters, often merging into large blisters. Hives can appear and disappear after a while, but often the disease begins to recur, and the rash recurs over several weeks, months, or years.
The signs of urticarial outwardly resemble stinging nettle burns (hence the name), the blisters have a varied shape with rounded edges and sizes from a match head to the area of the palm. Hives can cover small areas as well as large areas on the body: back, legs, arms, face, chest and abdomen. Urticaria disappears without a trace. Quincke edema is considered a type of urticaria and is often referred to as giant urticaria. The only difference is that with Quincke edema, not blisters are formed, but swellings that take up a large space.
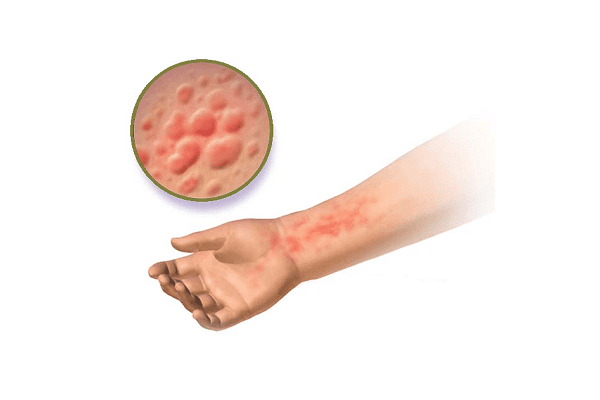
By its nature, urticaria is an immediate-type allergic reaction that develops under the influence of an increased release of active substances into the body: histamine, serotonin, bradykinin and other mediators. These substances cause increased vascular permeability and edema.
The causes of urticaria are varied:
- Food ingredients or the food itself
- Medicines
- Insect bites
- Hypersensitivity to cold, heat, sunlight
- Mechanical irritants (clothes, shoes, gloves, workwear items)
- Infectious agents (bacteria, parasites, etc.)
- Emotional upheavals (with an emotional outburst, acetylcholine is released, which is a mediator (transmitter) of nervous excitement at different levels and parts of the nervous system)
- Heredity
- Pathological work of internal organs
Urticaria treatment.
With acute urticaria, treatment is carried out with antihistamines according to the schemes indicated in the instructions for dibazol, tavegil, suprastin and other desensitizing drugs. In the case of Quincke edema, first aid is given. The suspected allergen is excluded from the use, an analysis is carried out for allergens.
Chronic urticaria requires special attention. It is a chronically recurrent illness with relapses lasting weeks (years). It is characterized by the formation of blisters (existing no more than 24 hours), collapsing and reappearing. Chronic urticaria treatment carried out by antagonists or blockers of H1-receptors. Some of these groups of drugs (diphenylhydramine, promethazine, chloropyramide, clemastine) have an effect similar to that of atropine (cause tachycardia, reduce the secretion and motility of the digestive system, increase bronchial obstruction, cause dilated pupils and many other side effects), which must be taken into account. Selective antihistamines of the second generation have fewer side effects and greater advantages. In difficult cases, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. Physiotherapeutic treatment of chronic urticaria (PUVA - therapy, UV-A irradiation) shows successful results in some patients, except for cases when urticaria occurs as a reaction to thermal stimuli or sunlight.
There is such a type of urticaria as cholinergic urticaria , which develops as a result of the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This type of urticaria does not respond to treatment with antihistamines, but requires the appointment of sedatives and anticholinergics.
In any case, when a recurrence of urticaria occurs, the true (and not hypothetical) causes that provoke it should be established, and only after that the treatment should be prescribed, otherwise it may be ineffective.

Read

Read



























