Dermatology >>>> Atopic cheilitis
Atopic cheilitis.

As a result of the body's reaction to allergens of various origins in the area of the red border of the lips and on the skin around the lips, an inflammatory process develops - atopic cheilitis, which can be one of the early symptoms of the development of atopic dermatitis. The red border of the lips begins to swell, peel off, dry out, crack, erythema forms on the lips - limited areas of a reddish color, lichenization of the lip tissues develops (tissue compaction and strengthening of its pattern). There is a burning sensation, itching, soreness in the area of the lips (the mucous membrane of the lips is not involved in the process). The typical location of atopic cheilitis is tissue damage mainly in the corners of the mouth.
The causes of atopic cheilitis may be related to:
- with a genetic predisposition of the body to allergies,
- with a decrease in the body's immune responses,
- with disorders of the digestive tract,
- with endocrine pathologies,
- with microbiocenosis disorders - dysbiosis.
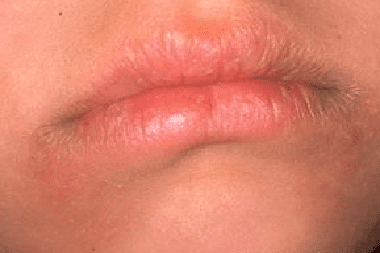
Most often, signs of atopic cheilitis occurs in childhood and adolescence, and now it is increasingly common among the older population up to 40 years of age and older. This suggests that allergization of the body may be associated with the consumption of foods containing substances that trigger an allergic reaction, with harmful work and living in an atmosphere contaminated with toxic substances, with prolonged and frequent stress loads on the body that weaken the immune system.
Atopic cheilitis is a disease characterized by seasonal manifestations (in cold periods of time - autumn, winter, early spring) and the possibility of spontaneous healing after puberty (there are rarely relapses of the disease). The diagnosis of "atopic cheilitis" is made on the basis of a visual examination of the state of the red border of the lips, histological studies and differential diagnosis with other diseases similar in symptomatology: some forms of cheilitis (exfoliative, allergic, actinic), seizures, lupus erythematosus.
Treatment of atopic cheilitis is aimed at reducing the sensitization of the body by taking antihistamines (tavegil, suprastin, diazolin and others), histaglobulin, to relieve inflammation - corticosteroids (topically in the form of ointments), sedatives, tranquilizers. Vitamin therapy is carried out (preparations of group B, vitamin A and vitamin E). The success of treatment largely depends on adherence to the diet - excluding potential food allergens from the diet (sweets, chocolate, strawberries, citrus fruits, canned vegetables and fruits, smoked meats, etc.). It is necessary to avoid the use of materials that provoke allergies, pollen, dust in everyday life .

Read

Read



























