Dentistry >>>> Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis.

The inflammatory process that develops in the surface layer of the oral mucosa and is accompanied by the formation of aft (erosions) is called "aphthous stomatitis". Aphtha is a defect of the epithelium of an oval or round shape up to 1 cm in size, located on an inflamed area of the mucous membrane, covered with a fibrinous coating of white or yellowish color and surrounded by a bright red rim around the perimeter. Afta can be located on the inner side of the lip, cheek, on the tongue, on the lateral surface of the tongue, on the mucous membrane of the alveolar process, in the palate. Aphthae are painful and cause a burning sensation in the mouth.
Aphthous stomatitis is accompanied by fever, enlarged lymph nodes, profuse salivation. According to the degree of intensity of the developing process, acute aphthous stomatitis and chronic aphthous stomatitis are distinguished (it is of a sluggish nature and is accompanied by an alternation of exacerbations and remissions).

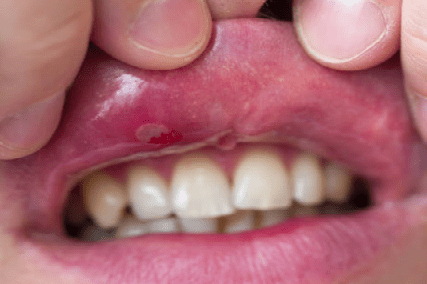
The causes of aphthous stomatitis are associated with specific disorders of the immune system, which poorly recognizes a chemical or biochemical structure (for example, a molecule of a chemical substance or a toxin of microorganisms), perceives it as foreign and activates lymphocytes.
Often, aphthous stomatitis develops as a result of trauma (violation of the integrity of the oral mucosa) - chemical or thermal burns, damage by sharp edges of teeth, dentures, a hard brush, hard elements of food or biting.
The presence of viral infectious agents in the body often causes aphthous stomatitis (for example, herpes infection, immunodeficiency virus, foot and mouth disease virus).
Lowered immunity is a predisposing factor for the onset of aphthous stomatitis.
Sometimes avitaminosis or hypovitaminosis can provoke the development of aphthous stomatitis.
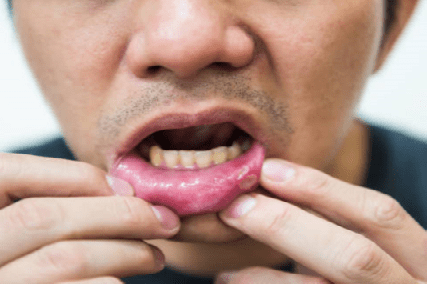
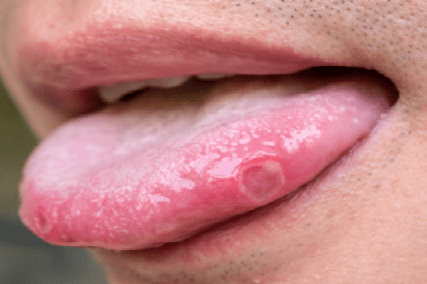
After 7-10 days, the aphthae heals on their own without scarring. But decreased immune responses and the presence of chronic infection can support the process and delay healing time. In such cases, consultation with a general dentist or mucosal specialist is necessary.
Medical treatment of aphthous stomatitis includes antiviral and antifungal therapy, immunostimulating agents, vitamin therapy, rinsing with antiseptic solutions or infusions from plants – antiseptics .
Local pain relievers are used (spray with lidocaine), proteolytic enzymes to remove necrotic plaque. After eating and rinsing, the location of the aphthae is lubricated with keratoplastic preparations to accelerate the regeneration of the mucous membrane (for example: sea buckthorn oil, karatolin, aekol).
According to indications, antihistamines are used, in severe cases, corticosteroids are prescribed in the form of applications to the sites of mucosal lesions.
With aphthous stomatitis, you must follow a diet:
- do not eat too hot food and drinks;
- exclude spicy, sour and salty foods during tissue healing;
- stop smoking temporarily;
- refuse to drink alcoholic beverages for the duration of treatment.

Read

Read


























