Ophthalmology >>>> Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis.
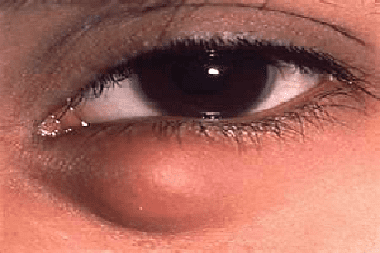
Narrowing or blocking of the nasolacrimal canal provokes the disease dacryocystitis - an inflammatory process in the lacrimal sac with accumulation of lacrimal contents, congestion, infection, suppuration and separation of purulent contents. Developing in an acute form, dacryocystitis can acquire a chronic course if adequate treatment is not carried out on time.
Dacryocystitis usually develops unilaterally and has typical symptoms. The inner corner of the eye turns red, swells, there is a sharp pain in the lacrimal sac, the inflammatory process is accompanied by constant lacrimation. The eye slit can be narrowed; when pressing on the area of the lacrimal sac, pus can be released with the lacrimal fluid. Severe inflammation affects the general condition of the body: it causes general weakness, headache, and increases body temperature.
With dacryocystitis, there is a possibility of the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby tissues, and through the bloodstream of the spread of infection, for this reason, the treatment of dacryocystitis is carried out in a hospital. With a significant accumulation of pus in the lacrimal sac, a surgical opening is performed in order to create an outflow of pus, drainage is installed, and washing with solutions of antibacterial agents and proteolytic enzymes is performed. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve inflammation.
Blockage of the nasolacrimal canal is eliminated by dacryocystorhinostomy - creating an anastomosis (passage) between the nasal cavity and the lacrimal sac for the outflow of tear fluid into the nasal cavity. The incision is made from the outside, at the inner corner of the eye.

Read

Read



























