Musculoskeletal system >>>> Myositis
Myositis.
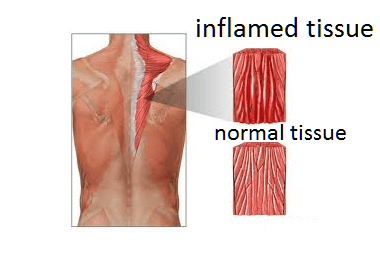
Inflammatory processes occurring in the muscles, accompanied by muscle weakness or excessive tension, having a different etiology, are called myositis. Myositis affects precisely the skeletal muscles. According to the form of the course, the disease is divided into acute myositis or chronic myositis. Moreover, the acute form often gives rise to chronic attacks. In terms of the degree of distribution, it can be local or diffuse (many muscle groups are involved). By location, myositis of the cervical spine, myositis of the thoracic spine, myositis of the lumbar spine, myositis of the muscles of the extremities are distinguished.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of myositis:
- Drafts
- Muscle injury
- Convulsions
- Muscle overstrain associated with an uncomfortable position of the body or excessive stress on certain muscle groups
- Different degrees of curvature of the spine
- Hypothermia
- Intoxication
- Infectious diseases
- Parasitic diseases (helminths)
- Complications of other diseases (arthritis, rheumatism, osteochondrosis)
- Autoimmune diseases
The characteristic signs of myositis are :
- Pain sensations (sharp, aching, may increase over time) - especially noticeable when moving in certain parts of the body: turning the head, tilting and turning the body, taking deep breaths
- Puffiness
- Hyperemia of the affected area (redness)
- In places of pain that has arisen, compacted muscles are felt (as if overstrained)
- Muscle dysfunctions at the site of inflammation (reduction or decrease in tone, or in cases of prolonged chronic myositis, muscle tissue atrophy, its decrease)
- The purulent course of the disease is accompanied by a temperature.
Treatment of myositis includes symptomatic therapy and therapy associated with the etiology of the disease. In severe cases, preliminary electromyography is often performed, which most accurately reflects the condition of the skeletal muscles.
Symptomatic therapy includes:
- pain relievers (various local and general analgesics - often used as injections)
- anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal) - Ortofen (and its synonyms, Diclofenac, Voltaren, Naklofen), Indomethacin, Ketonal, Nurofen (Ibuprofen)
- physiotherapy - warming compresses, ointments, rubbing, UHF, electrophoresis, massage (categorically contraindicated for purulent myositis)
- exercise therapy
Basic therapy related to the cause of the disease:
- antiparasitic agents or antibiotics when indicated
- for purulent processes - surgical intervention
- in the case of autoimmune causes - immunosuppressants, glucocorticosteroids

Read

Read



























