Medicine questions >>>> Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage.

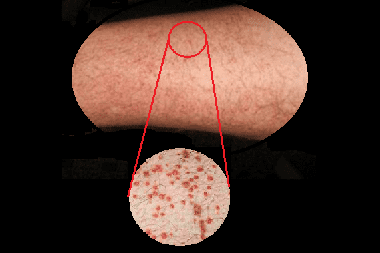
Hemorrhage in translation from ancient Greek means bleeding, in fact it is a hemorrhage through the walls of blood vessels into the interstitial space, tissues and body cavities. Most often, the term "hemorrhage" is used in cases when they want to emphasize that there is multiple destruction of the walls of blood vessels and, accordingly, multiple hemorrhages. Impacts of an endogenous or exogenous nature lead to an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall, which is accompanied by multiple hemorrhages in the tissue and interstitial space. Pinpoint capillary hemorrhages are called hemorrhagic petechiae. Merged hemorrhagic petechiae lead to the formation of hemorrhagic purpura - a red spot protruding on the skin (mucous membranes). Multiple patches of purpura form a hemorrhagic rash on the skin.
The causes of hemorrhage can be different:
- Destructive actions of the vital activity of bacteria, viruses, fungi;
- Microscopic parasites that perforate the walls of blood vessels;
- Chemicals of endogenous or exogenous origin that violate the integrity of the walls of blood vessels;
- Hereditary anomaly, manifested in the form of increased fragility of the vascular walls.
Treatment of hemorrhage requires identifying the causes that led to large-scale damage to the blood vessels and treatment of the underlying disease that caused large-scale hemorrhages. In the treatment of hemorrhage, special attention is paid to the rheological properties of blood and, in particular, the rate of its coagulation, since it is the rate of blood coagulation that affects the outcome of hemorrhage, the volume of blood flow out of the bed and its loss.

Read

Read



























