Healing diets >>>> Diet for periodontal disease
Diet for periodontal disease
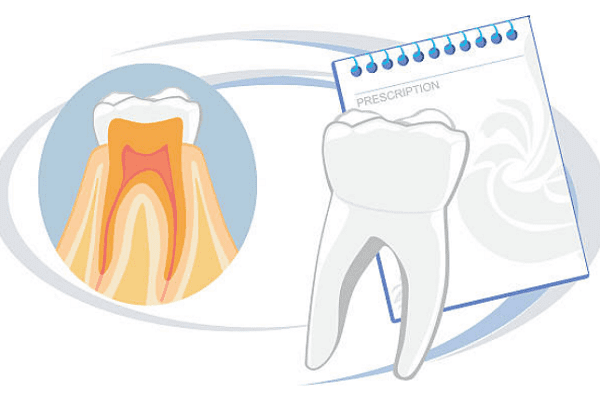
The basis of the disease Periodontal disease is dystrophic processes, accompanied by weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, acute and chronic inflammation of the perigingival pocket, resorption of bone tissue not only of the periodontal space, but also of the entire alveolar process. It is the ligamentous apparatus that is responsible for the stability of teeth under chewing load. But with periodontal disease, teeth lose their stable position, gain varying degrees of mobility, and begin to loosen. Their endurance decreases during the chewing process. Due to the fact that periodontal disease is complex and has a multi-stage nature, dietary nutrition for periodontal disease is compiled depending on what stage of the disease the patient is going through. At different stages of the development of periodontal disease, the stability of teeth varies. For this reason, food is chosen based on the current condition of the teeth, and a set of products and the possibility of their preparation are selected that are suitable for different stages of the disease.
At the early stage of development of periodontal disease, structural changes in bone tissue are not yet visible during radiographic studies. But unpleasant processes may develop in the gums and in the periodontal area, for example, loss of tissue sensitivity (feeling of gum numbness), itching. The teeth are still held quite firmly by the ligamentous apparatus, but can no longer withstand excessive chewing load.
During this period, it makes sense to give up the bad habit of continuously c masticate chewing gum or chewing candies, you should give up candies with a viscous and sticky consistency, and hard candies. You should stop biting into solid foods (for example, a cucumber, an apple, a pear, a large piece of sausage or meat - all these foods are cut into small pieces and placed in the mouth to be chewed in small portions). You should switch to cooking ground or cut into small pieces of meat, to eating less hard fried foods, and give preference to boiled and pureed foods. You should not get carried away with eating whole nut kernels or whole dried fruits (they are consumed in the form of crushed and finely chopped). At its core, the diet at this stage of periodontal disease contains a lot of fortified foods, foods that support the immune system, as well as foods containing fairly large doses of vitamin D and the trace element Calcium. It is necessary to drink a lot of vitamin juices and eat natural vegetables and fruits that contain vitamins.
At the next stage of periodontal disease, the phenomena of gingivitis are already present , the gum tissue becomes loose, the periodontal gum pockets may become inflamed, and purulent processes in the gums may develop up to the occurrence of abscesses.
The diet for periodontal disease during this period of the disease is gentle and supportive. During this period, it is important not to injure the gums with hard, poorly crushed food and not to overload the periodontium with hard pieces of food and products that require a large chewing load, for example, chewing nut kernels, crackers, hard baked goods (bagels, hard biscuits, hard cookies), especially hard ones bread crusts. In your diet, you should avoid eating hard dried fish and hard sausages, and do not chew raw carrots or other types of root vegetables that are usually allowed to be eaten raw.
At the last stage of periodontal disease, loosening and unstable position of the teeth, loss of gums and bone tissue of the alveolar process become obvious. The necks and roots of the teeth are exposed, it seems that the teeth are “growing”, but in fact the gums are moving away from their usual level (sinking), and their volume is decreasing.
During this period, special requirements are imposed on the diet, which consist of eating only ground and pureed foods (for example, pates, chopped meat dishes), boiled hard vegetables, grated fresh vegetables and fruits (carrots, apples, pears). The diet for periodontal disease of the third stage does not involve the consumption of boiled meat cartilage, hard meats, dried fish and various dried products. It is better to eat your favorite dishes in a paste or puree form, so as not to put additional strain on your mobile teeth. You should know that hard and excessively dry food very often injures the gum pockets of the teeth, and this worsens the overall picture of the disease and is an additional traumatic factor.
Since the development of periodontal disease is a multifactorial process, and is often associated with age-related characteristics of the state of the body as a whole, the task of the diet for periodontal disease is to prevent additional loads on the periodontal teeth, eliminate traumatic factors during the chewing process, supportive vitamin therapy and immunotherapy of the body.

Read

Read



























