Cardiovascular system >>>> Allergic vasculitis
Allergic vasculitis.

Allergic vasculitis develops due to infection and the development of inflammation as a result of exposure to an endogenous or exogenous allergen. The role of an allergen can be played by a bacterium, virus, fungus, chemical, radiation. Infectious allergens enter the vascular wall from foci of chronic infection, with frequent respiratory diseases, chronic pyelonephritis, adnexitis, etc.
Allergic vasculitis differs from systemic vasculitis in that with allergic vasculitis, the walls of the vessels of the skin and subcutaneous tissue are affected, the vascular system of the internal organs does not suffer. Distinguish between superficial allergic vasculitis, in which the walls of the capillaries are affected, and deep allergic vasculitis, in which the vessels of medium and large sections are affected.
Allergic vasculitis is very diverse in its external manifestations:
- hemosiderosis,
- hemorrhagic,
- nodular,
- erythema nodosum,
- polymorphic (various rashes).
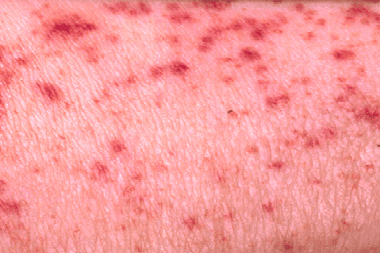
Diagnosis of allergic vasculitis is carried out by examining the tissues of the skin and subcutaneous layer, a blood test is performed for the presence of antigen-antibody complexes in it. Due to the variety of signs of allergic vasculitis, differential diagnosis is carried out with other diseases similar in symptoms.
Treatment of allergic vasculitis involves the use of antihistamines and desensitizing drugs. Apply drugs to strengthen the vascular wall, ascorbic acid, aminocaproic acid. Vascular preparations are used to maintain vascular tone. Anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed if necessary.

Read

Read



























