Cardiovascular system >>>> Aneurysm
Aneurysm.
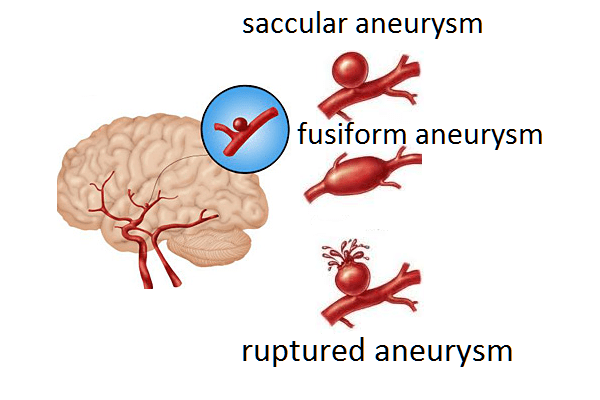
Aneurysm is a pathological change in the lumen of blood vessels (arteries, veins) due to their local expansion (protrusion). The vascular wall becomes thinner, stretches more than usual and does not return to its original state. The sites of vasodilation in aneurysm have a different appearance, depending on what they received the names and aneurysms: saccular (single-chamber and multi-chamber), fusiform (fusiform). There are so-called arteriovenous aneurysms that appear in the vessels of the brain and look like a tangled tangle of arterial and venous vessels in contact with each other.
The causes of aneurysm are associated with structural abnormalities of the vascular wall caused by congenital anomalies or acquired diseases: vascular injuries, medial vascular necrosis (necrosis of the middle vascular membrane, causing dissection of the vessel wall), arteriosclerosis, hypertension, syphilis and many other diseases that give rise to aneurysm.
The most common aneurysm sites are:
- Arteries of the brain
- A heart
- Aorta
- Peripheral blood vessels (eg, limb vessels)
Symptoms that give reason to suspect the presence of an aneurysm:
- Headache,
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness,
- Speech disorders
- Disorders of consciousness
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
Symptoms that give reason to suspect a ruptured aneurysm:
- Severe headache attack
- Deterioration of vision
- Pain in the back of the head
- Pain in the eyes,
- Loss of consciousness.
Aneurysm is a very dangerous phenomenon, since up to a certain point it can not manifest itself in any way, but its rupture can end in death. Therefore, for the successful prevention of irreparable consequences, timely detection of the aneurysm, its diagnosis and adequate treatment are required.
There are several methods for diagnosing aneurysm:
Angiography is a radiopaque study of blood vessels, helps to reveal the degree of vasoconstriction / dilation or destruction of blood vessels, and specifies the location of the aneurysm. The angiography method consists in injecting a contrast agent into the bloodstream through a special flexible catheter, with preliminary anesthesia.
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to view the vessels in a three-dimensional image or two-dimensional cross-section.
Computed tomography - allows you to identify the location of the aneurysm and determine, digitally fix the gap and the presence of bleeding.
Treatment of aneurysm depends on the type, location of the aneurysm, its size, the likelihood of rupture, the health status and age of the patient, and also takes into account the health risks associated with treatment methods.
Several surgical methods are used to treat aneurysms:
One of the methods of endovascular embolization involves the introduction of a metal stent-graft into the vessel at the site of a possible rupture of the aneurysm. The stent graft is placed in such a way as to shield the wall of the vessel with the aneurysm from blood pressure. The blood flow passes through the stent graft without affecting the aneurysm, thus protecting it from rupture.
The second method of endovascular embolization, coiling, is based on the introduction of a thin-section platinum wire into the area of the vessel dilatation with the help of a catheter, which is located in the form of a ball in the aneurysm zone, making it difficult for blood to pass through the desired vessel, and thereby turns it off from the bloodstream.
Aneurysm clipping - implies the application of a clip - a clip - to the body or neck of the aneurysm.

Read

Read



























