Digestive system >>>> Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids.
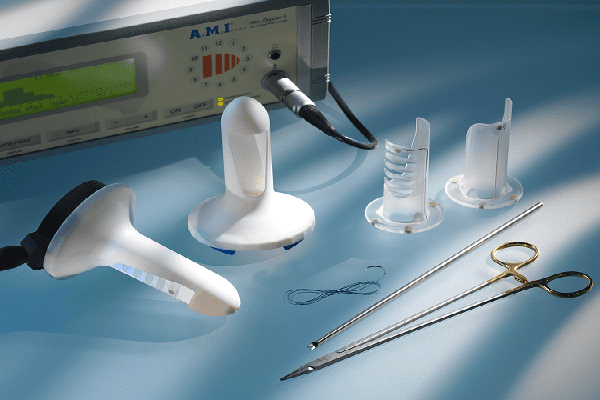
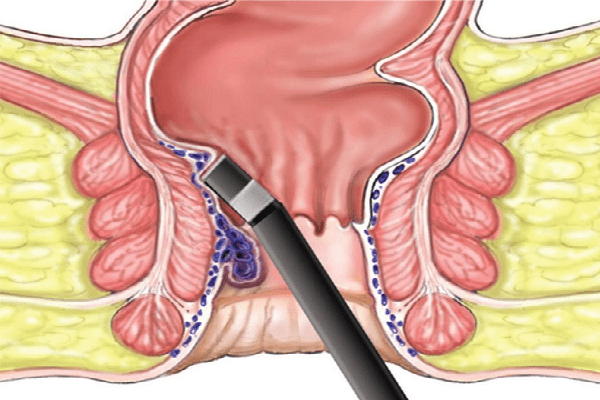
With the ineffectiveness of drug therapy in the treatment of hemorrhoids, surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is used. The choice of options for surgical intervention for hemorrhoids depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of complexity of its course. Hemorrhoids can occur in four stages:
- First: hemorrhoids of small size appear, protrude into the lumen of the rectum, but not beyond it (not visible in the lumen and outside the anus).
- Second: hemorrhoids can fall out during the act of defecation, but return to their previous position on their own.
- Third: hemorrhoids fall out of the rectal lumen and do not return to their original position (they are adjusted manually).
- Fourth: hemorrhoids are greatly increased in size and no longer return to the rectal lumen and are not manually adjusted, but are constantly located outside the anus.
Among the numerous methods of surgical intervention for hemorrhoids, if possible, it is worth giving preference to minimally invasive methods (that is, carried out with the least degree of trauma to the surrounding tissues and a low degree of complications after the intervention procedure).
Minimally invasive surgical methods for the treatment of hemorrhoids:
- Electrocoagulation is carried out during the first or second stage of the disease and is aimed at cauterizing the vessels with electrodes, through which blood flows into the formed hemorrhoid.
- Infrared photocoagulation is designed to block blood vessels that provide blood flow to the hemorrhoid using a stream of infrared radiation that cauterizes the vessels. The operation is indicated for the first and second stages of hemorrhoids.
- Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids is based on the property of certain chemicals to cause collapse (adhesion) of the vessels supplying the hemorrhoid with blood, as a result of which the lumens in the vessel close, and the hemorrhoid stops growing, atrophies and falls off. Sonotherapy is effective in the first and second stages of the disease.
- Ligation of hemorrhoids consists in throwing a ligature (ring) onto the node, which compresses the vessels of the blood supply to the node and after several sessions, the node is removed. Ligation is suitable for the second and third stages of hemorrhoids.
- Dysarterization of hemorrhoids is designed for the third and fourth stages of hemorrhoids. An operation of this kind is carried out under the supervision of an ultrasound scan. Its essence lies in the ligation of the vessels supplying the hemorrhoidal node with blood, slightly above their entry into the node.
A full-fledged surgical intervention (hemorrhoidectomy) is performed at the third and fourth stages of the disease, in cases for which minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids were ineffective.
Hemorrhoidectomy is open and closed. The first is carried out in uncomplicated cases of hemorrhoids and ends with suturing wounds after removing the nodes (it can be performed on an outpatient basis, that is, without being in the hospital), and the second is carried out when hemorrhoids are complicated by other diseases (paraproctitis, anal fissure) and its completion is associated with leaving wounds after removal open (not sewn) until they heal on their own (requires being in a hospital).
There are several main methods on which surgery is based in the course of a full-fledged surgical intervention:
- Operation Longo (hemorrhoidopexy), in which a circular removal of the submucosal - mucous layer above the area of the hemorrhoidal nodes is performed, followed by suturing the wound, due to which they are pulled higher, their blood supply is disrupted, are gradually replaced by connective tissue. Inpatient treatment takes 3-4 days. The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia.
- Hemorrhoidectomy according to Milligan – Morgan. This is an open hemorrhoidectomy, in which, after removing the nodes, the wounds are not sutured, but remain open until complete self-healing. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and requires hospitalization for 3-7 days. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
- The Parks operation, in which the mucous membrane under the node is cut, the damaged tissue is removed and the wound is sutured. Requires hospitalization, is carried out under anesthesia and is technically difficult.
In addition to the methods described, there are multiple modifications of them that are used according to indications.

Read

Read



























