Digestive system >>>> Hirschsprung disease
Hirschsprung disease.
Hirschsprung disease is a congenital anomaly in the innervation of the lower part of the large intestine (agangliosis is a lack or absence of ganglia in certain parts of the intestine that are responsible for the peristalsis of the intestinal walls).
Hirschsprung disease leads to disturbances in the digestive processes, or rather, to disturbances in the intestinal parts responsible for the evacuation of feces, which is accompanied by prolonged constipation (one-time emptyings in five to seven days or less, in severe cases only after an enema). According to statistical studies, half of patients suffering from Hirschsprung disease have gene mutations inherited from one of the family members.
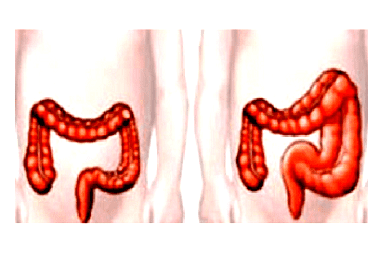
The disease makes itself felt from the first weeks of a child's life and without proper treatment leads to serious consequences. The child becomes restless, cries, suffers from constipation, begins to lose weight.
Signs of Hirschsprung disease appear from childhood:
- There is no urge to defecate,
- Emptying the bowel requires the use of an enema,
- Recurrent pain in the colon area,
- Flatulence and bloating,
- Education fecal stones,
- Signs of intoxication of the body (violation of the general condition, headaches, nausea).
Depending on the place of absence of ganglia in the walls of the large intestine, there are:
- rectal form (rectum is affected);
- rectosigmoidal form (part of the rectum and part of the sigmoid colon is affected); subtotal form (half of the large intestine is affected);
- total form (the entire large intestine is affected).
According to the severity of the course of the disease, there are:
- Compensated form (with a general satisfactory condition, regular constipation is observed),
- Subcompensated form (constipation is observed, anemia develops , body weight decreases),
- Decompensated form (intestinal obstruction develops , the nutritional process is disrupted and dystrophy develops).
Diagnosis is based on family history, colon tissue biopsy, colonoscopy, and irrigography. For the diagnosis, they rely on three symptoms characteristic of Hirschsprung disease: constipation, flatulence, and radiographically revealed enlargement of the loops of the large intestine.
Treatment of Hirschsprung disease requires surgical intervention in order to excise non-innervated areas of the large intestine, as well as expanded areas of the intestine. Conservative therapy (probiotics; diet with the participation of products that stimulate peristalsis, consumption of large volumes of liquid, vegetable fatty foods, fermented milk products; vitamin therapy with ascorbic acid, B vitamins, vitamin E; abdominal massage; siphon enemas; parenteral nutrition if the process of eating is disturbed ) are carried out as preparatory work preceding surgery.

Read

Read



























