Digestive system >>>> Colitis is a disease and symptom
Colitis is a disease and symptom.
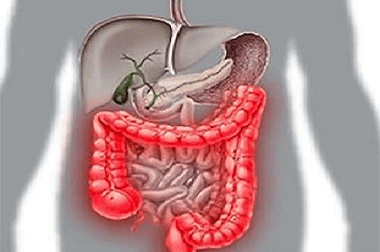
The large intestine, like other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, can be involved in various kinds of painful conditions. One of these conditions is colitis, an inflammatory process that develops in the mucous membrane lining the large intestine from the inside. It should be noted that the mucous membrane plays one of the main roles in the intestines. It is a haven for various types of microorganisms - saprophytes, participating in the processes of digestion and utilization of food components. And the inflammatory processes developing in its structures are an obstacle to the normal functioning of these microorganisms.
In addition to microbiocenosis in colitis, the peristalsis of the large intestine is disturbed, which complicates the evacuation functions of the gastrointestinal tract and leads to a number of other diseases directly related to the violation of the evacuation functions of the large intestine (dyskinesia of the large intestine, weakness of the large intestine, intestinal obstruction, tumors of the large intestine, diverticula of the large intestine, constipation, hemorrhoids, intestinal stones).
Colitis is a disease of the large intestine, varied in the causes and conditions of the course, but similar in signs and methods of treatment.
Distinguish between spastic colitis, erosive colitis, ulcerative colitis, nonspecific colitis, colitis caused by toxic or radiation damage, infectious colitis, ischemic colitis and many others.
There are many reasons for colitis in any of its manifestations:
- Specific and nonspecific infectious agents that settle in the mucous membrane of the large intestine and cause its toxic damage or disrupt the structure of intestinal tissues;
- Violation of the innervation of intestinal smooth muscles, which is responsible for the motor function of the colon;
- Chronic stress causing disruptions in the peristalsis of the large intestine;
- Dysbiosis, changing the ratio of beneficial and conditionally pathogenic microflora;
- Autoimmune disorders of the colon;
- Allergic reactions affecting digestion in the large intestine;
- Monotonous and unbalanced diet;
- Chemical and mechanical trauma to the walls of the large intestine.
By the nature of the course, colitis can be acute or chronic. Acute colitis develops most often with infectious diseases, when infectious agents have time to damage the mucous membrane of the large intestine. Acute colitis manifests itself in the form of disturbances in the formation of feces (diarrhea, followed by constipation and vice versa). In this case, a person feels cramps in the intestines, bloating, pain symptoms, very similar to those of appendicitis. Chills and even fever may occur. A change in the composition of feces can also join the main symptoms: blood and mucus in the feces, sometimes purulent discharge.
Chronic colitis is less severe, but no less painful. Chronic colitis is characterized by unstable fecal mass, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, frequent constipation, abdominal pain, and often the pain symptom is felt in the lower back (especially after sleep). Eating is accompanied by discomfort, heaviness in the abdomen and upset stools. Food is poorly digested. The belly swells up, growls.
With erosive and ulcerative forms of colitis, in addition to the symptoms of intestinal disorders, erosions and ulcers form on the mucous membrane lining the inner part of the large intestine, which do not heal for a long time and worsen to an even greater extent the condition of the person suffering from this disease. Ulcerations bleed (which is reflected in the presence of signs of blood in the feces), cause poorly tolerated pain that lasts for several hours, high fever and lead to a violation of the general condition of the sick person.
Colitis is diagnosed with the help of a colonoscopic examination, irrigoscopy (X-ray examination with the introduction of a radiopaque substance into the intestine).
Colitis requires persistent treatment. Colitis treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis (at home), and in difficult cases - in a hospital.
In addition to colitis, which is considered a disease, medicine is also faced with the signs of colitis, which are called "colitis syndrome". Colitis syndrome is a set of symptoms characteristic of the manifestations of colitis, but accompanying other diseases. Colitis syndrome accompanies functional diseases of the colon, disturbances in the blood supply to the intestines, inflammatory diseases of the small intestine, dysbiosis, acute intestinal infections, and can also result from the consumption of foods poor in fiber. In addition, colitis syndrome can be observed in people with a sedentary lifestyle or prone to deep and long-term experiences.
Colitis syndrome includes almost the entire set of signs of colitis as a full-fledged disease, the only difference is that colitis syndrome can be short-lived and resolves with the treatment of the underlying disease that caused it.

Read

Read



























