Digestive system >>>> Cachexia
Cachexia.
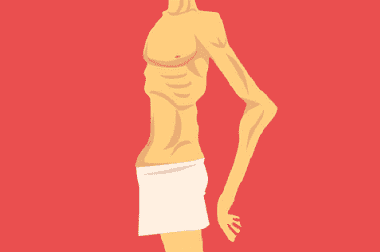
Cachexia is the extreme degree of depletion of the body, which is characterized by a sharp decrease in weight, general weakness, a violation of many physiological processes, including the work of the brain, which is reflected in a change in the mental state of the patient. Cachexia is considered a terminal condition, that is, deadly. According to statistics, cachexia has a high mortality rate.
Cachexia can develop against the background of forced or deliberate starvation, in cases of a number of diseases with severe somatic pathology (oncology, endocrine disorders, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, chronic pancreatitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, tuberculosis, alcoholism, chronic heart disease). failure, AIDS and others).
Signs of cachexia:
- Low body weight, less than 70% of the normal body weight,
- High rate of weight loss.
The mechanism of development of cachexia is associated with several factors:
- Insufficient intake of protein in the body during fasting, diseases of the oral cavity, pharynx or esophagus,
- Disruption of the processes of digestion and / or absorption,
- Accelerated metabolic degradation process in a number of diseases,
- Accelerated excretion of protein from the body in nephrotic syndrome, burn disease and in a number of other cases,
- Increased need for proteins during illness, after operations, infectious diseases.
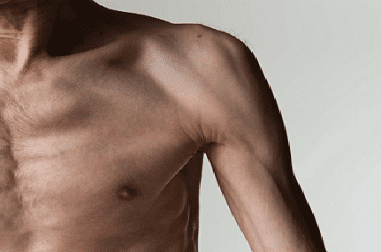
Diagnosis of cachexia is sometimes difficult, when, against the background of a decrease in muscle mass, adipose tissue remains, which distorts weight indicators, and cachectic edema can also develop , which changes the picture of external signs of exhaustion.
Treating cachexia is difficult because it often does not bring the desired results. The medical complex includes a full-fledged diet consisting of special mixtures selected in accordance with the possible pathologies of the patient's gastrointestinal tract (if enteral nutrition is impossible, parenteral nutrition methods are used by introducing infusion solutions). Enteral and parenteral nutrition are often combined to prevent the development of degenerative changes in the mucous layer of the gastrointestinal tract. Appetite stimulants and growth hormones, gluconeogenesis inhibitors, anticytokine drugs are used (clinical studies of the effect of such drugs are controversial).

Read

Read



























